home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides
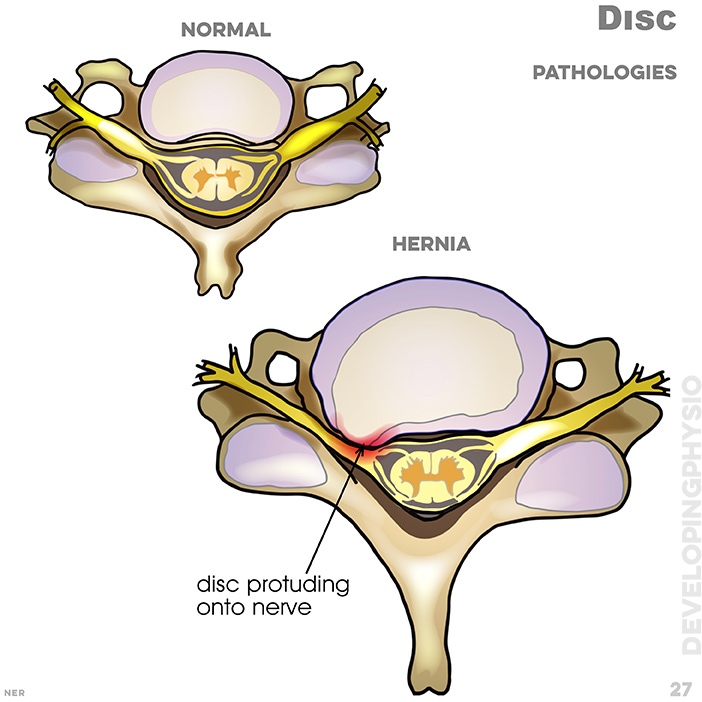
27. Disc pathologies: normal, hernia, disc protruding onto nerve
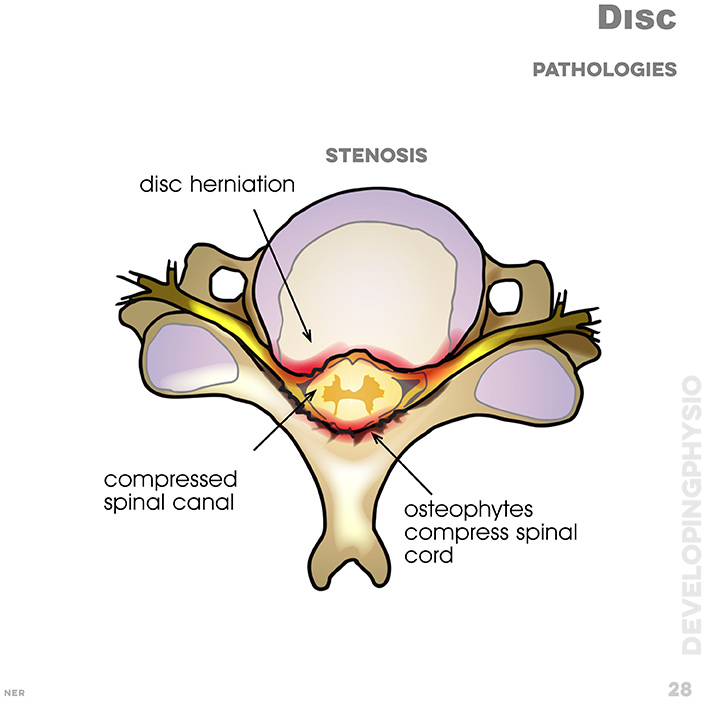
28. Disc pathologies - stenosis: disc herniation, compressed spinal canal, osteophytes compress spinal cord
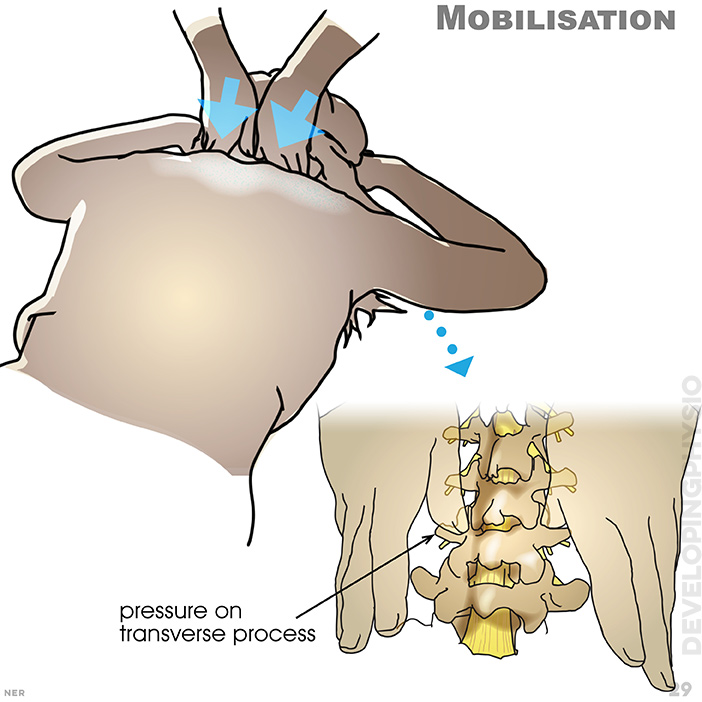
29. Mobilisation: pressure on transverse process
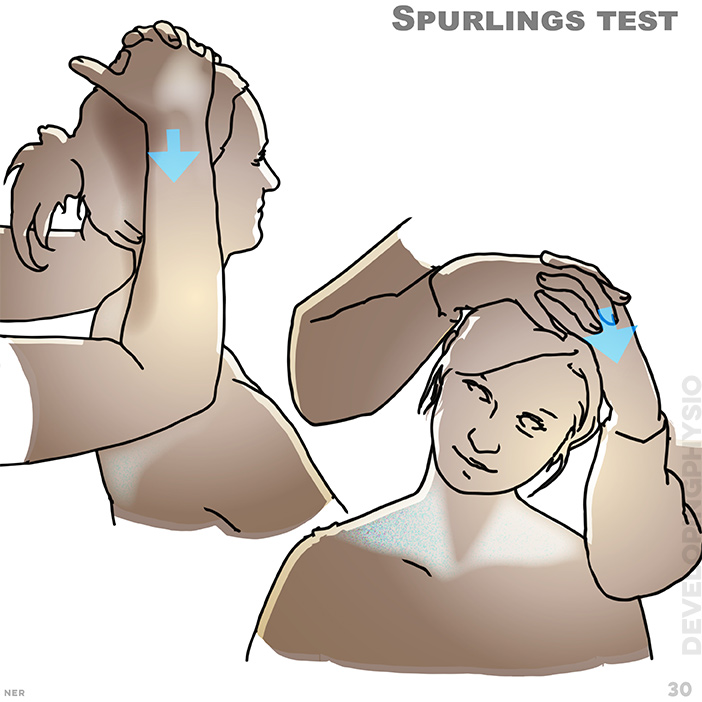
30. Spurlings's test: A positive test is when pain radiates in the pattern of a dermatome, indicating pain from a nerve root. downward pressure applied gently to place load on neck structure
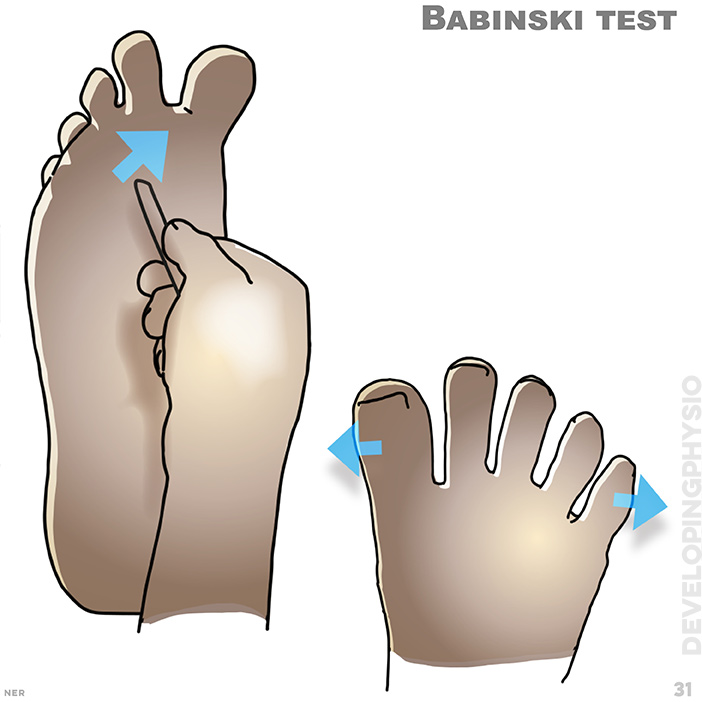
31. Babinski test: if toes splay in reflex this indicates a problem with the spinal cord/brain. sharp instrument along lateral border of the sole tests reflex
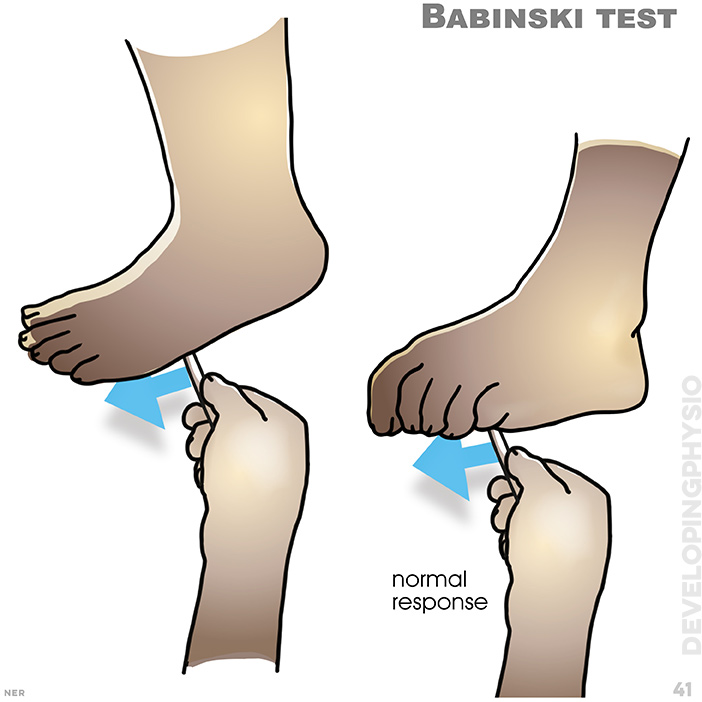
41. Babinski test: if toes curl down in reflex then this indicates a normal reaction
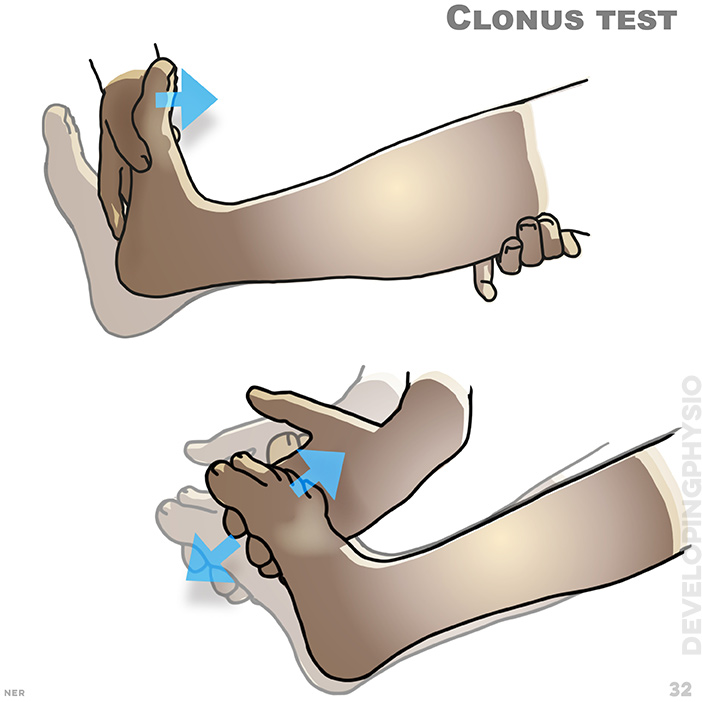
32. Clonus test: A positive test is when the foot shows rhythmic, uncontrolled movements, after being quickly and firmly bent upwards. It may indicate a a problem with the brain/spinal cord and require medical assessment
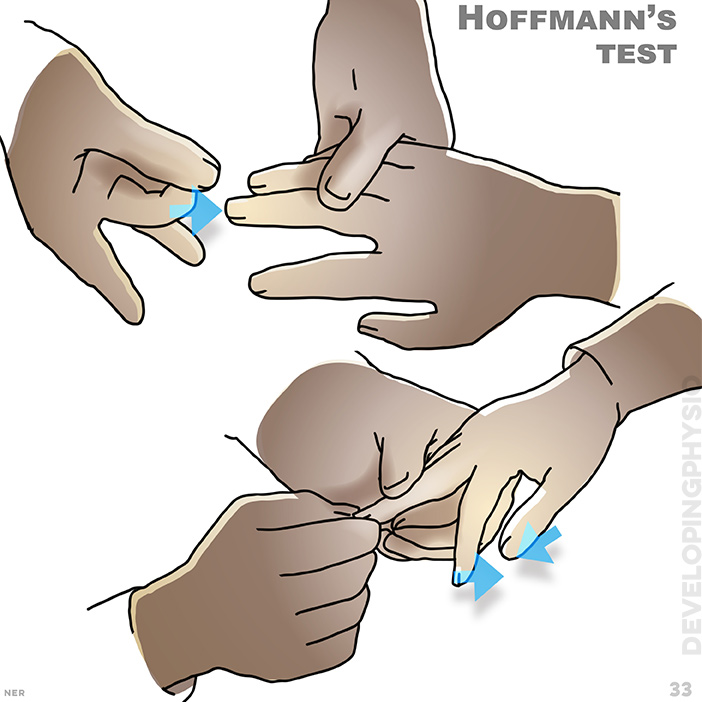
33. Hoffmann’s test: The test is done by tapping or flicking the nail of the middle finger. A positive sign is when thumb and index finger bend, and may indicate a spinal cord/ brain problem, requiring medical assistance.
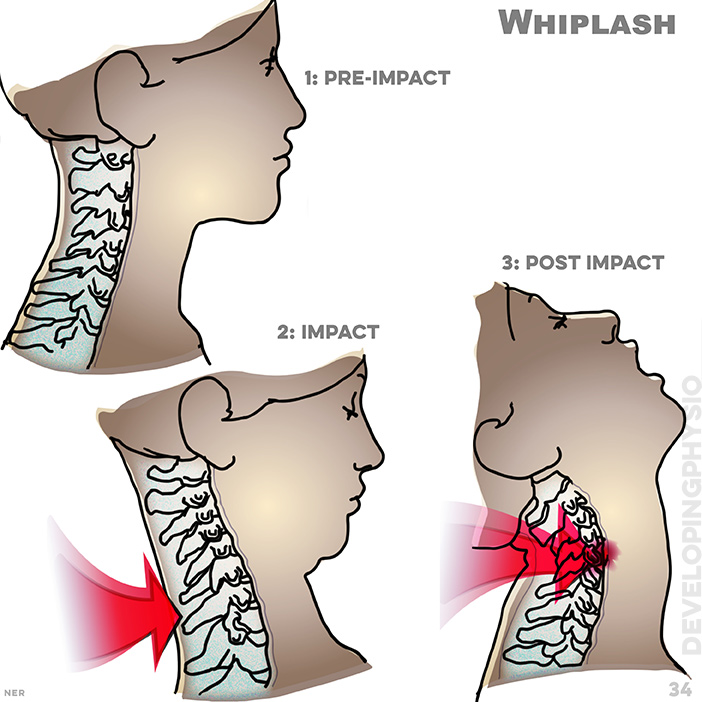
34. Whiplash: Whiplash is caused by sudden movement of the head forwards, backwards or sideways, overstretching tendons, ligaments and muscles in the neck. 1 - pre-impact, 2 - impact, 3 - post impact
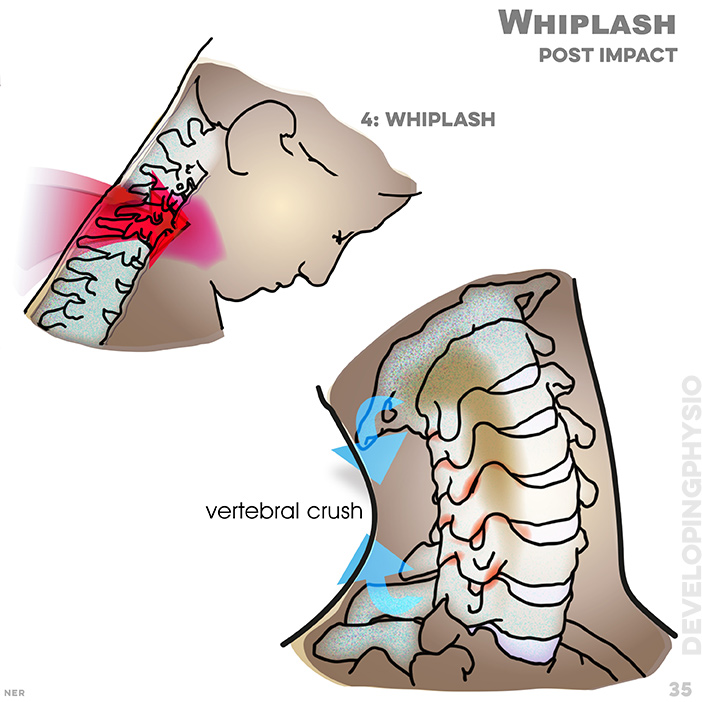
35. Whiplash - post impact: 4 - whiplash, vertebral crush
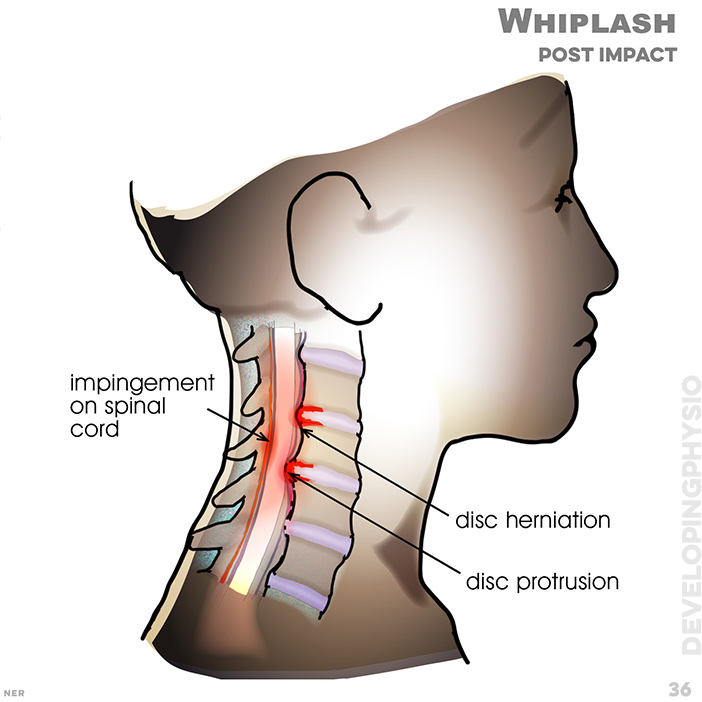
36. Whiplash - post impact: impingement on spnal cord, disc herniation, disc protrusion
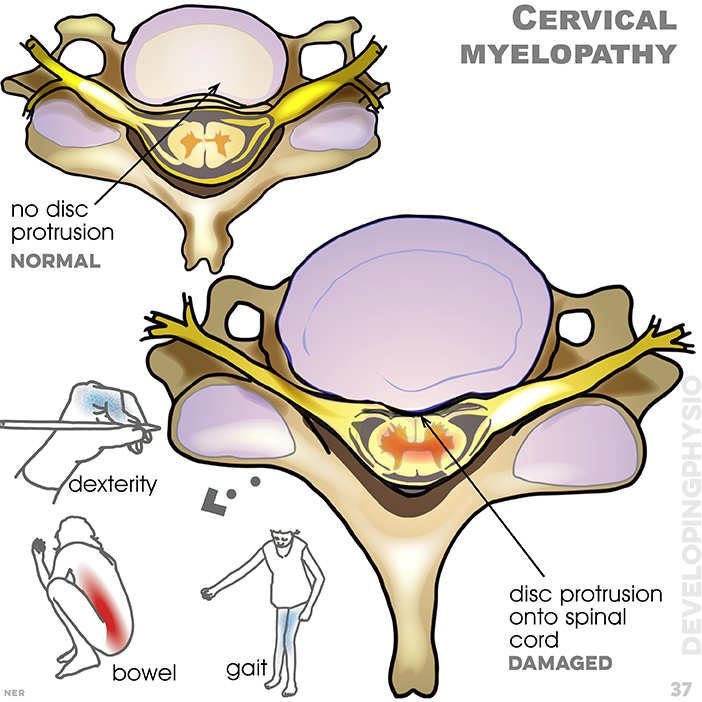
37. Cervical myelopathy: Cervical Myelopathy is a condition caused by narrowing of the spinal canal, leading to cord dysfunction. This could be caused by trauma, a large central prominent disc bulge or Rheumatoid Arthritis, and require medical assessment if possible. disc protrusion onto spinal cord
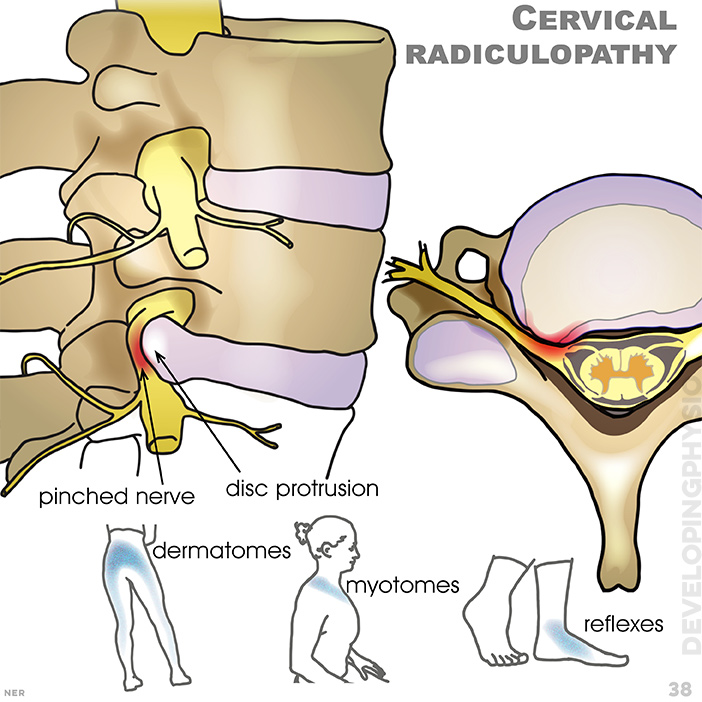
38. Cervical radiculopathy: Cervical Radiculopathy is a dysfunction of a nerve route in the cervical spine, usually caused by a disc bulge putting pressure on the nerve tissue exiting the spinal column. pinched nerve, disc protrusion, dermatomes, myotomes, reflexes
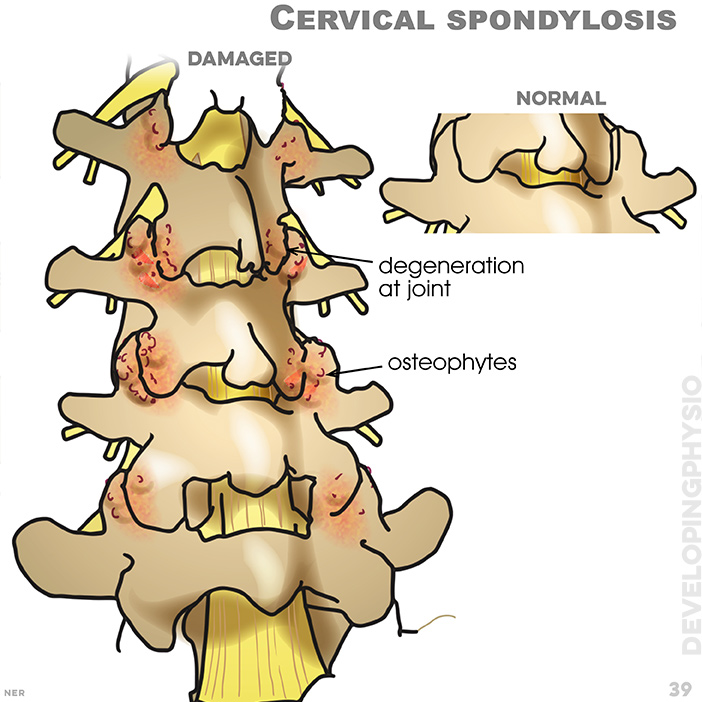
39. Cervical spondylosis (osteoarthritis) is the medical term for neck pain caused by age-related changes to bones and tissues. The most common symptoms are stiffness and headaches, primarily affecting people over 50 years old
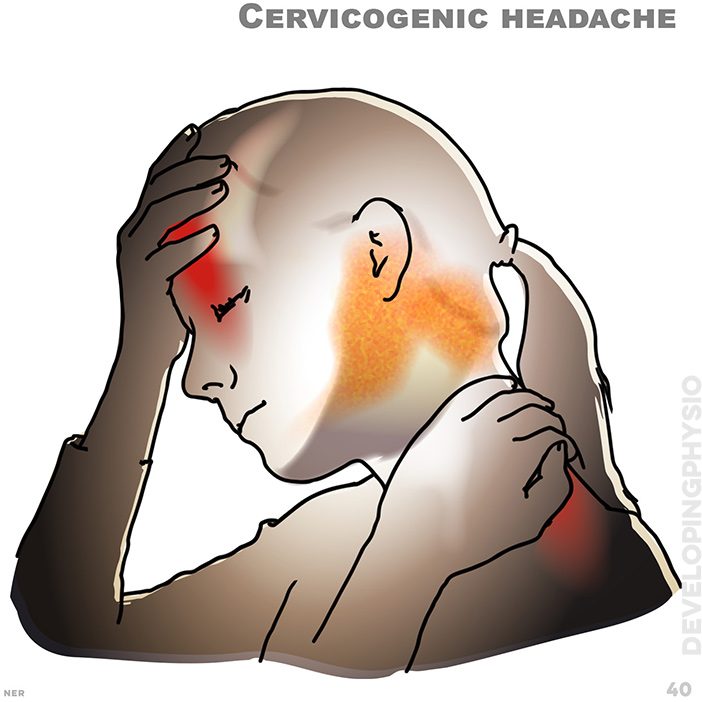
40. Cervicogenic headache: pain up the neck, at back of the jaw and above the eyes, accompanied by symptoms such as muscle tenderness or decreased range of motion, often precipitated by sustained or abnormal posture. Can also happen after a trauma