home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides
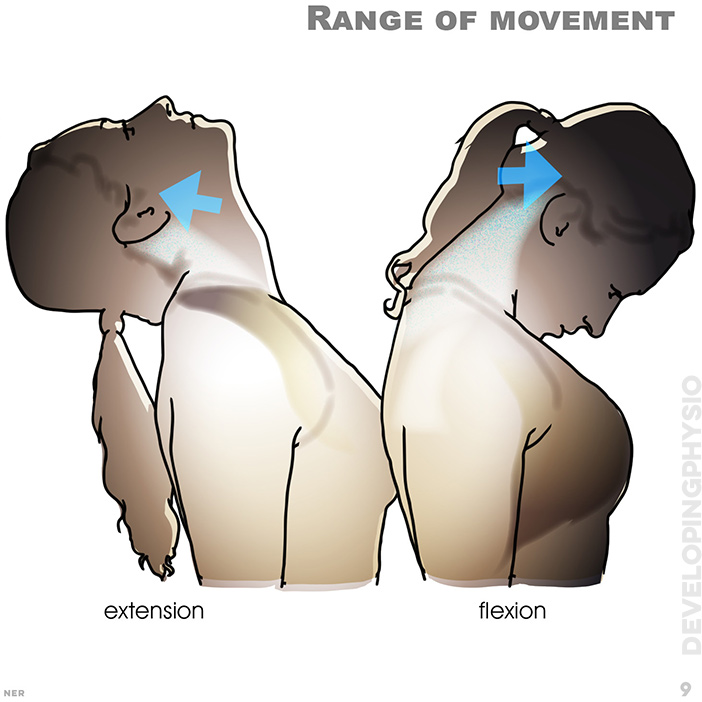
9. Range of movement: extension, flexion
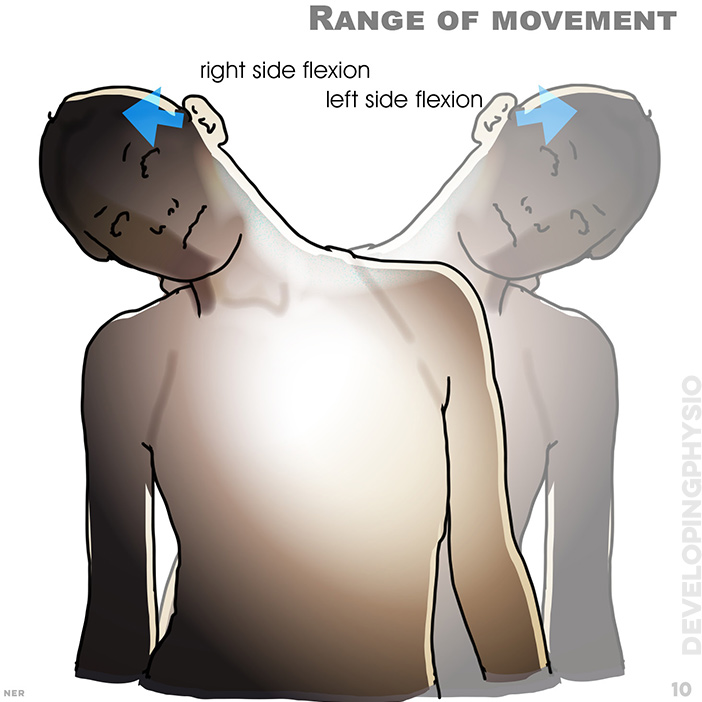
10. Range of movement: right side flexion, left side flexion
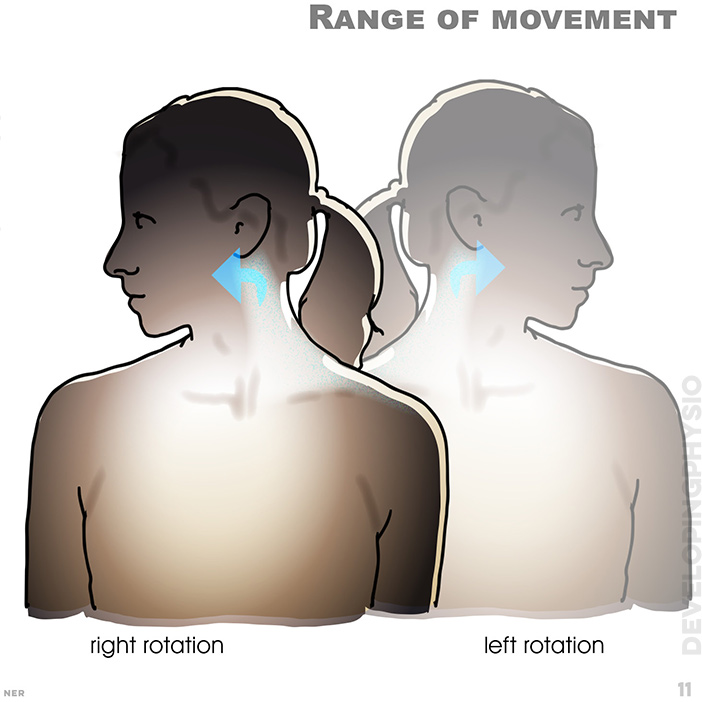
11. Range of movement: right rotation, left rotation
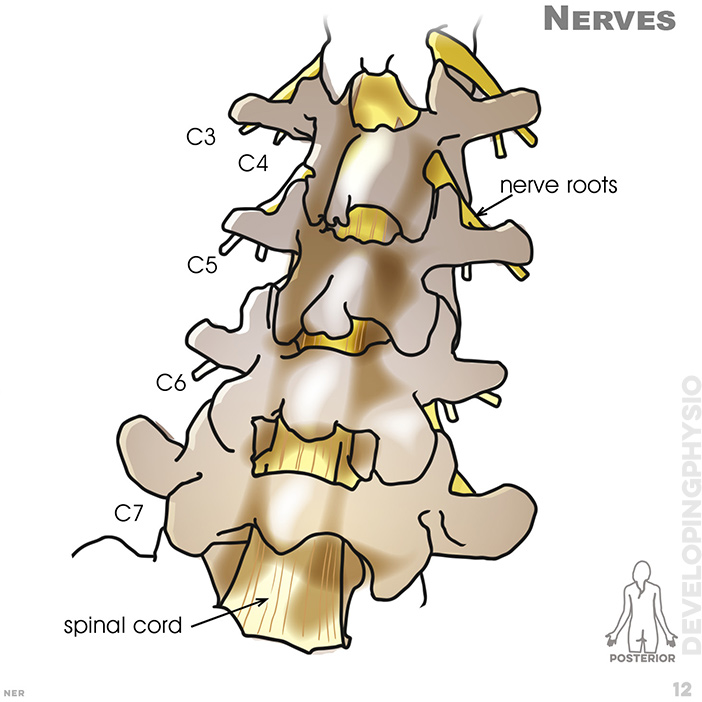
12. Nerves: nerve roots, spinal cord
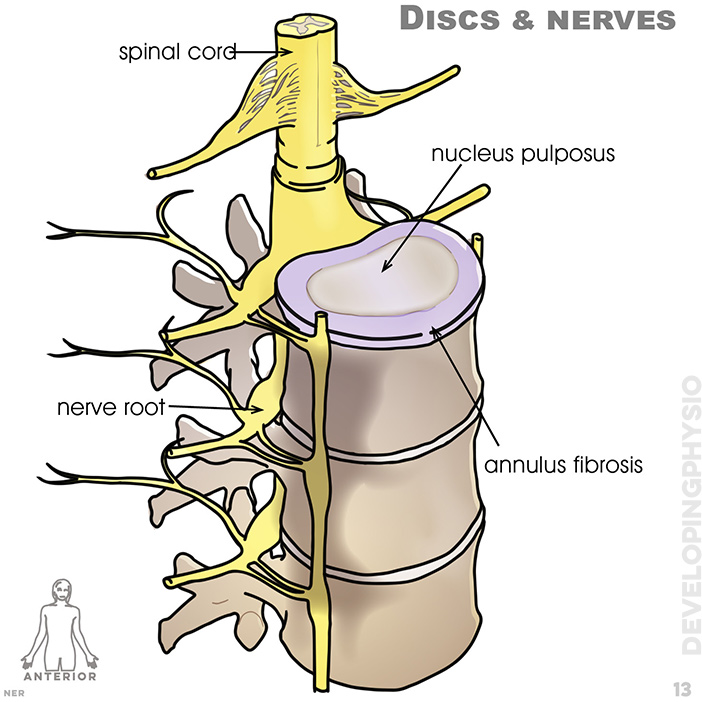
13. Discs and nerves: spinal cord, nucleus puposus, annulus fibrosis, nerve root
14. Discs and nerves: spinal cord, nerve root, nerve root ganglion
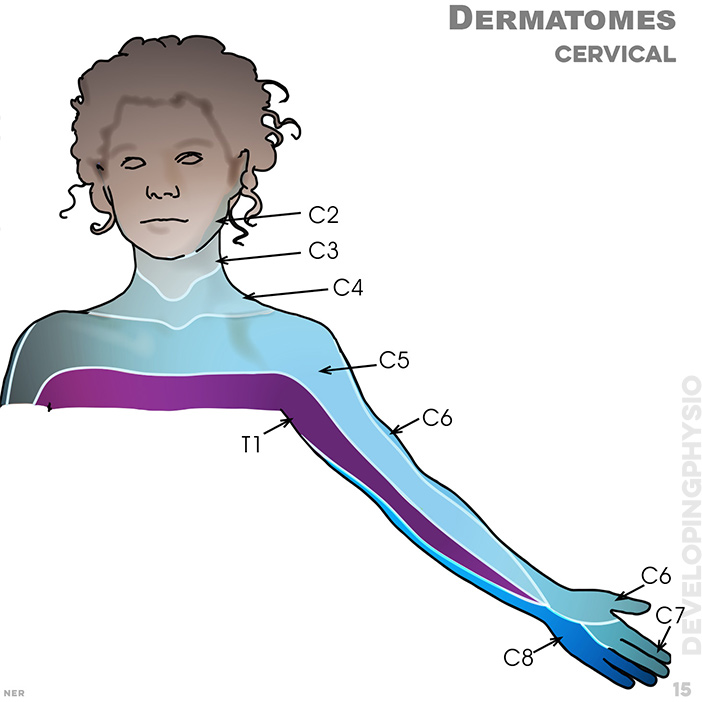
15. Dermatomes (cervical): C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, T1
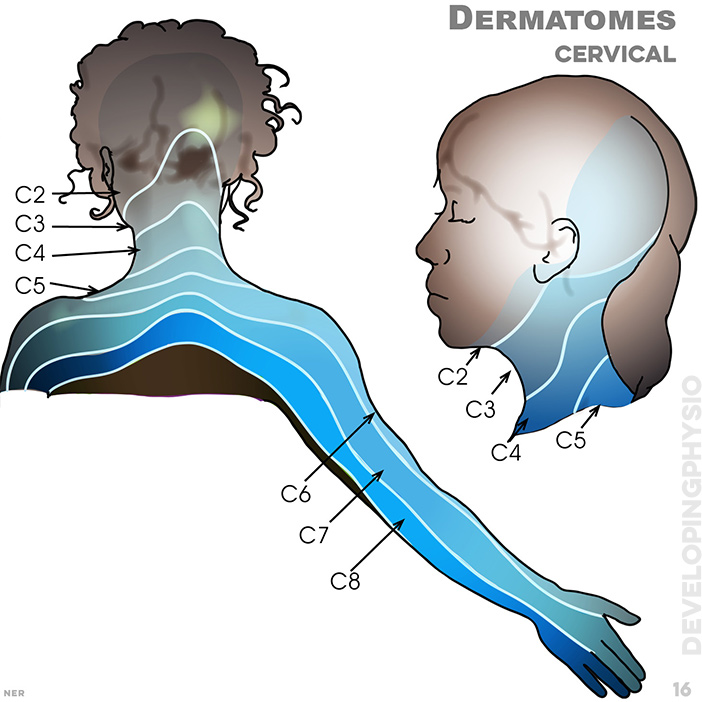
16. Dermatomes (cervical): C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8
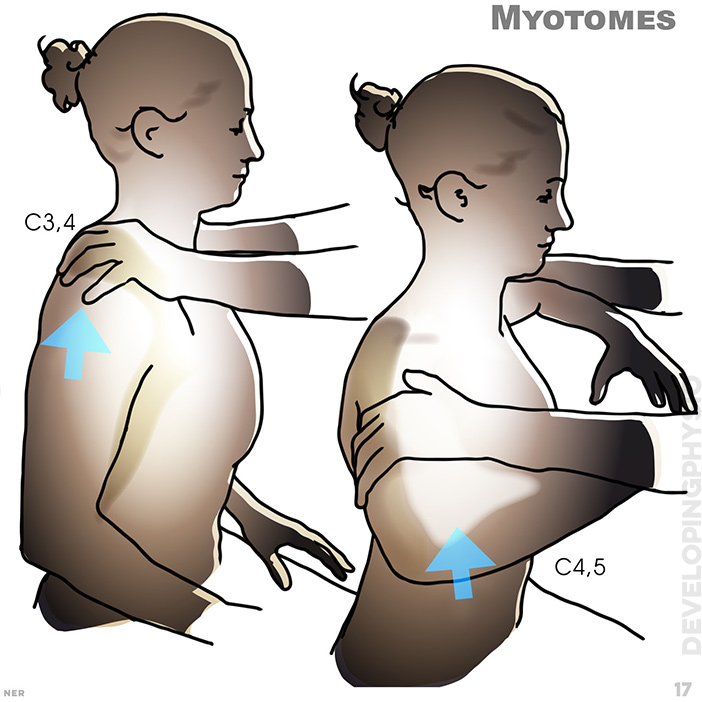
17.Myotomes: C3, 4; C4, 5
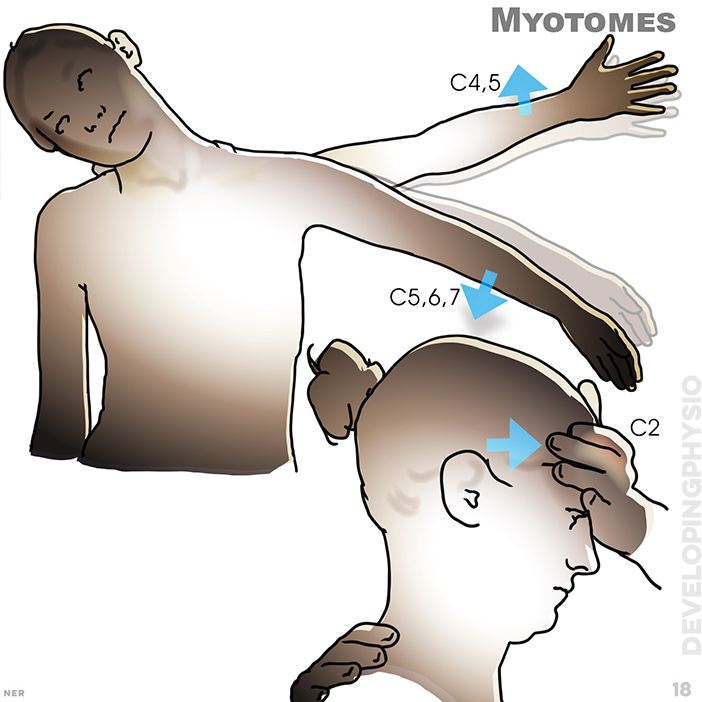
18. Myotomes: C4, 5 C5, 6, 7: C2
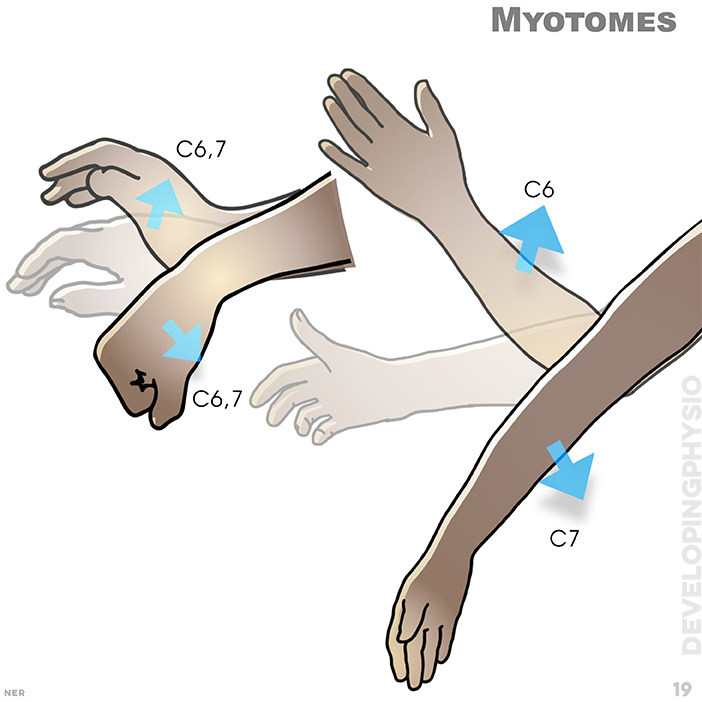
19.Myotomes: C6, 7
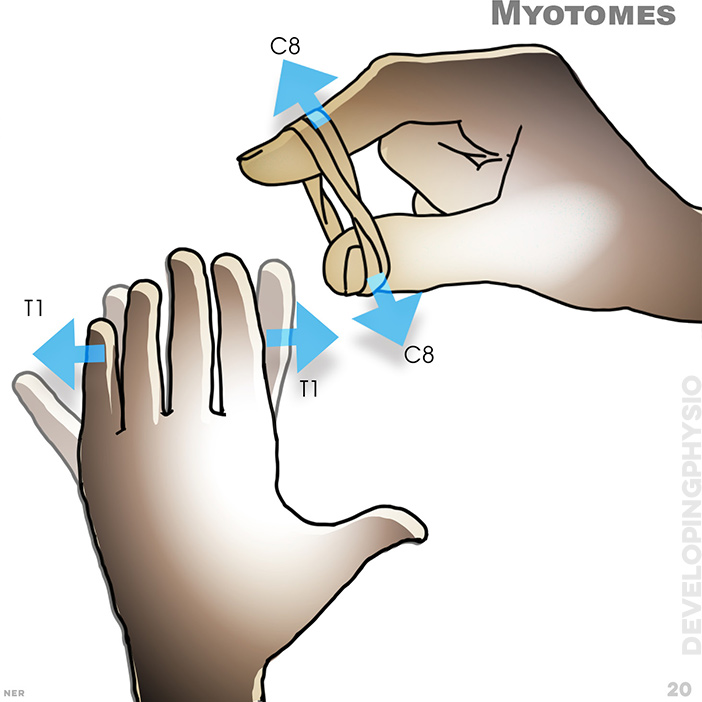
20. Myotomes: C8, T1
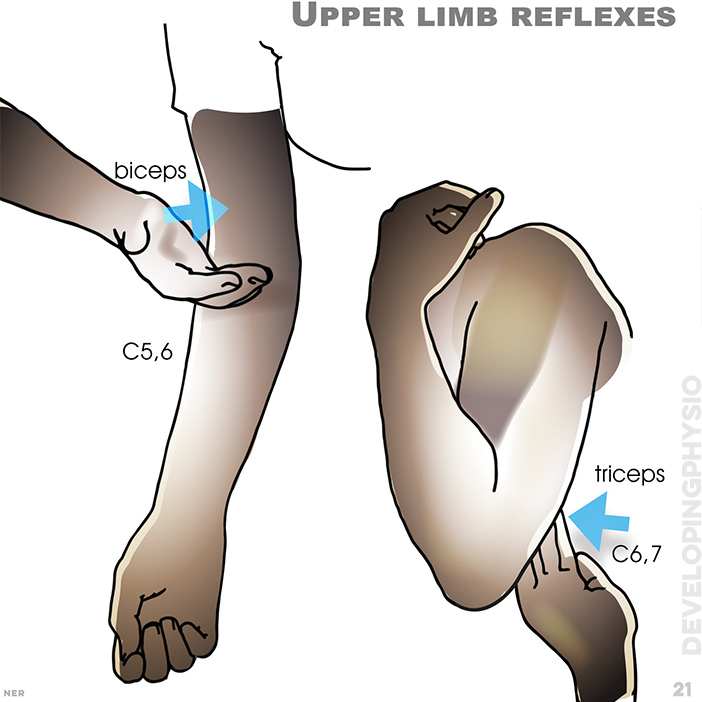
21. Upper limb reflexes: A normal response is a jerk/twitch response of the limb being tested. Slow or no response shows nerve compression on C5-6 (biceps) and C6-7 (triceps). biceps, C5, 6; triceps, C6, 7
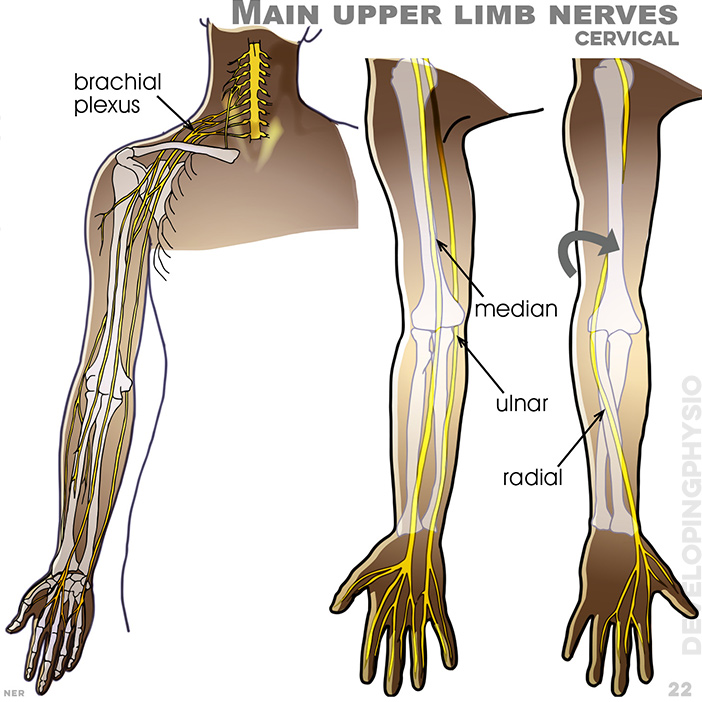
22. Main upper limb nerves (cervical): brachial plexus, median, ulnar, radial
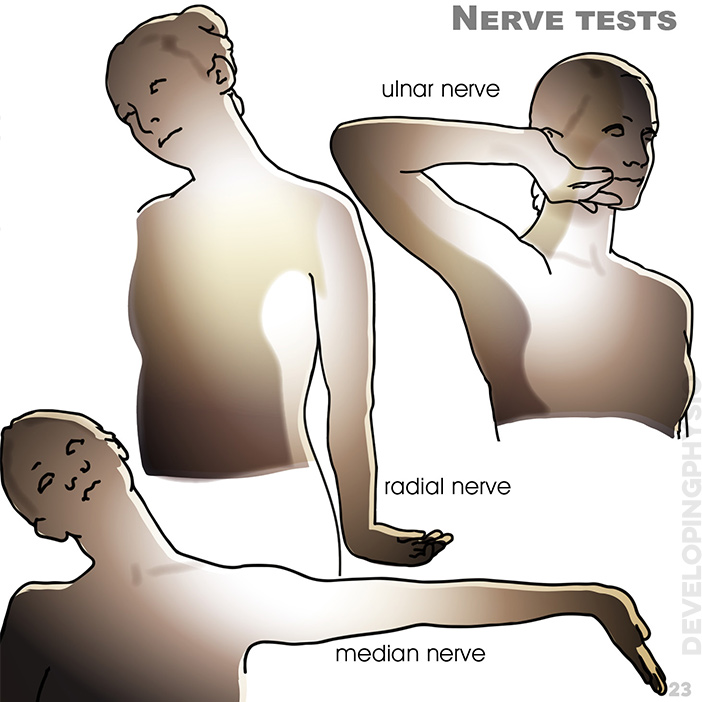
23. Nerve tests: ulnar nerve, radial nerve, median nerve

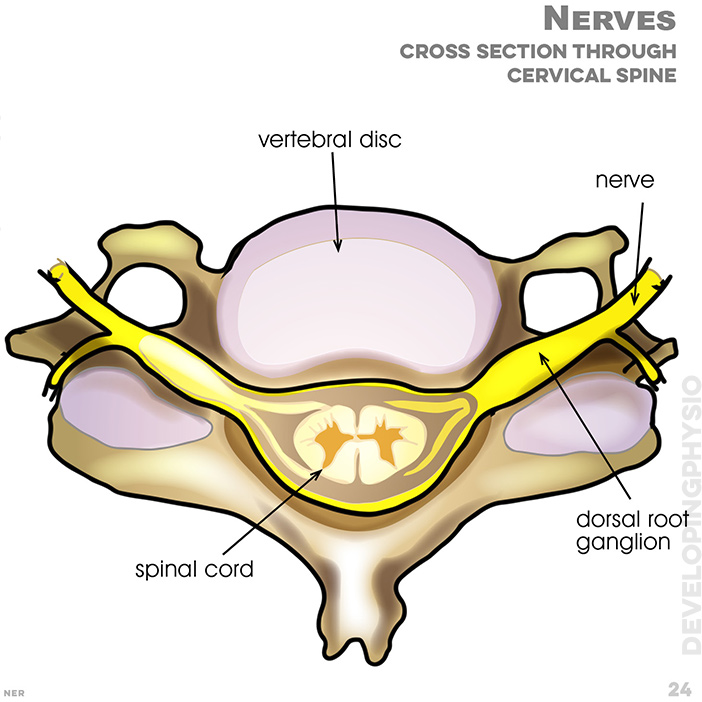
24. Nerves - cross section through cervical spine: vertebral disc, nerve, dorsal root ganglion, spinal cord

12. Soft tissue healing. Acute inflammation blood clot forms, tissue disruption. 72 hours. Regeneration clot shrinks, new fibrous tissue forms. 72 hours – 6/8 weeks. Re-modelling tissue fibres become organised. 6/8 weeks – 6/12 months.
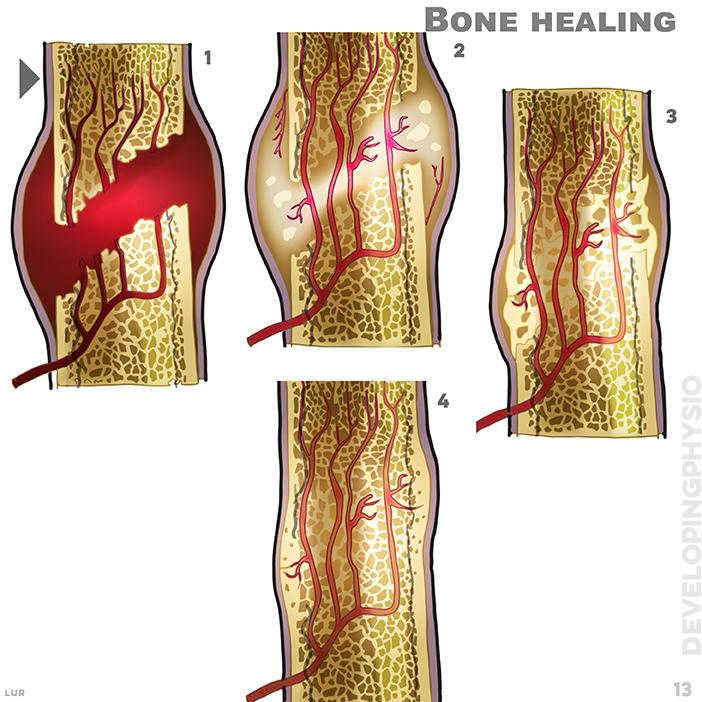
13. Bone healing: haematoma, week 1. soft callus, week 2 to 3. hard callus weeks 4 to 16. remodelling week 17 onwards