home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides

12. Soft tissue healing. Acute inflammation blood clot forms, tissue disruption. 72 hours. Regeneration clot shrinks, new fibrous tissue forms. 72 hours – 6/8 weeks. Re-modelling tissue fibres become organised. 6/8 weeks – 6/12 months.
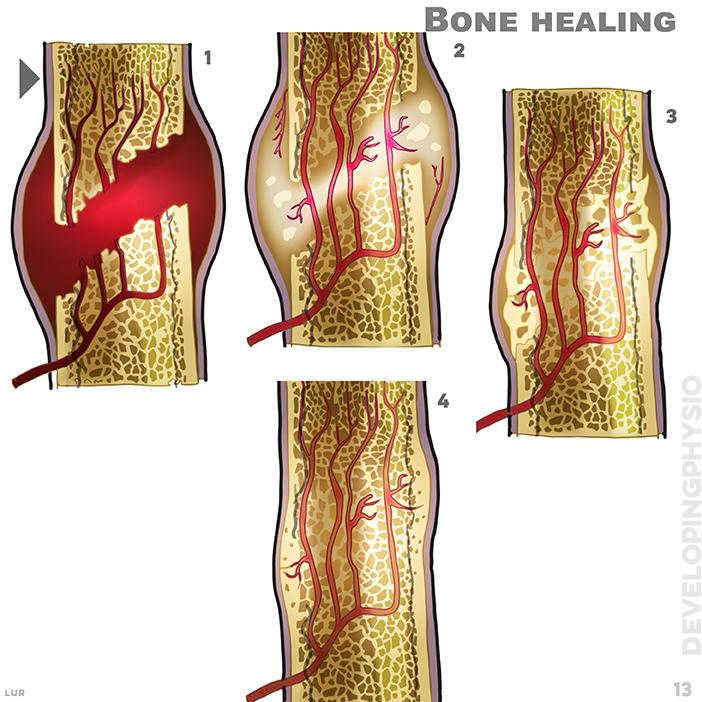
13. Bone healing: haematoma, week 1. soft callus, week 2 to 3. hard callus weeks 4 to 16. remodelling week 17 onwards
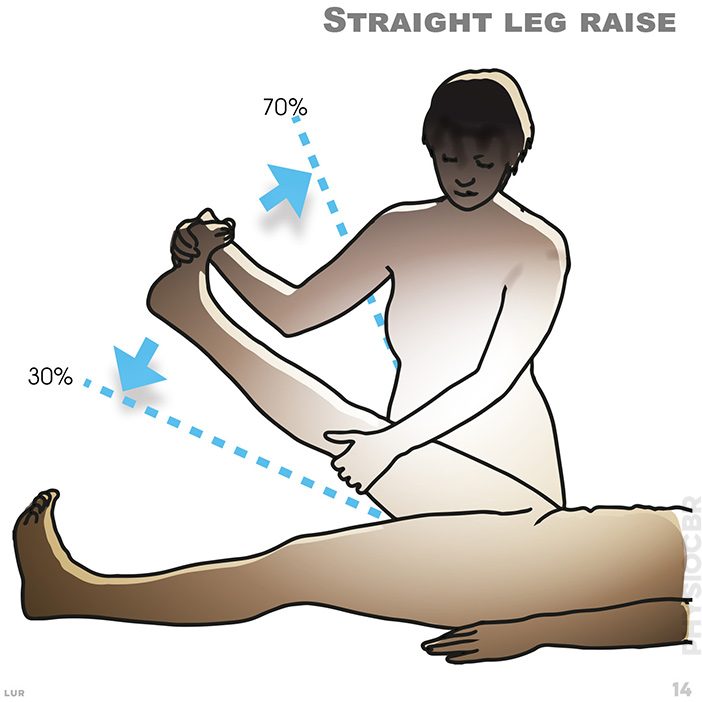
14. The Straight Leg Raise (SLR) test is a neurodynamic test to check the mechanical movement of the neurological tissues as well as their sensitivity to stress or compression. A positive result is most commonly found in a disc prolapse or bulge.
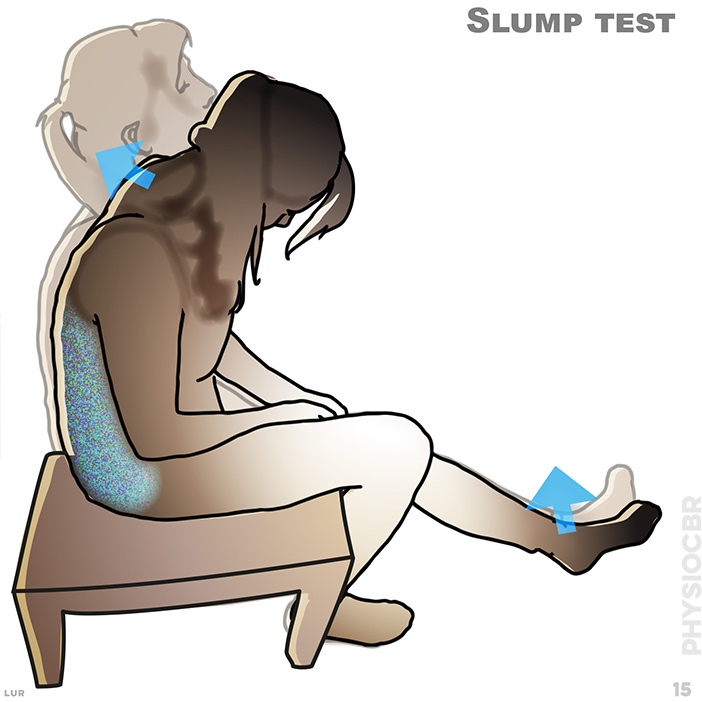
15. A slump test is used to assess whether a disc bulge, neural tension or altered neural dynamics are causing the patients symptoms.
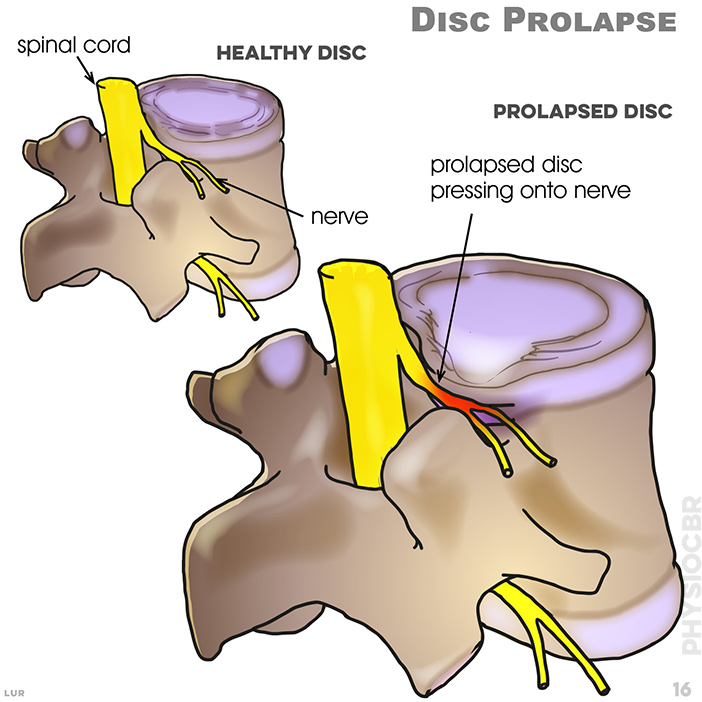
16. Disc prolapse. prolapse disc pressing onto nerve. When bending forwards, pressure on the spine forces the disc backwards towards the nerve roots.
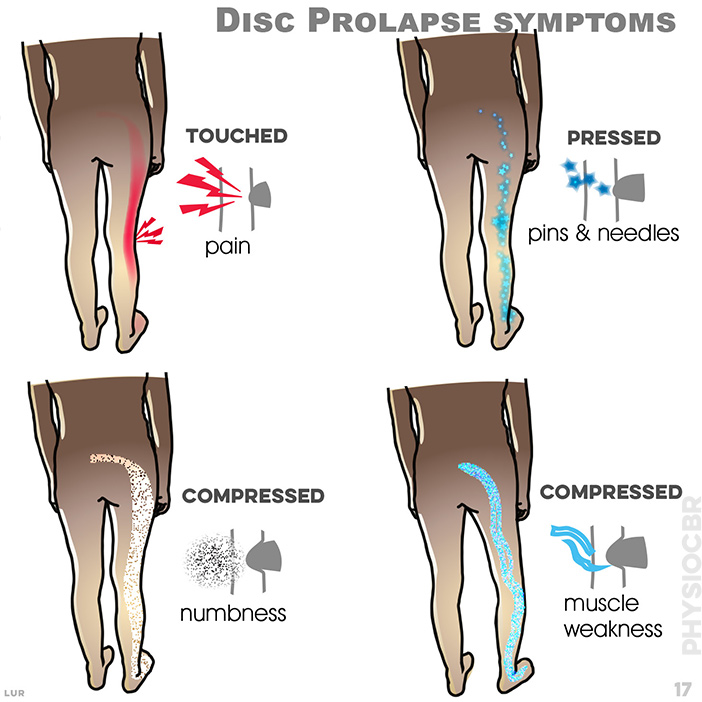
17. Prolapse can lead to the nerve tissue being compressed, affecting the patient’s strength, sensation and reflexes.
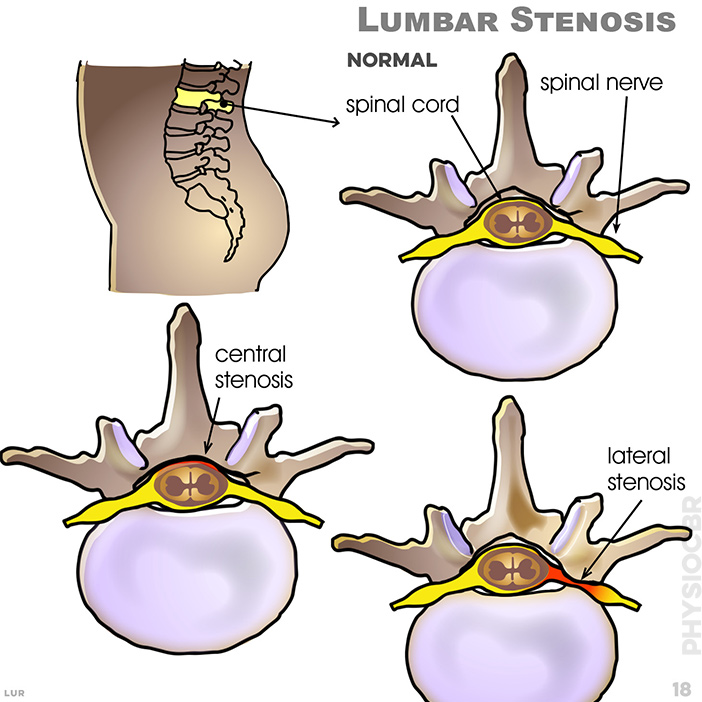
18.Lumbar stenosis: This is an abnormal narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal. It may occur in any of the regions of the spine where bone growth pushes into the spinal cord.
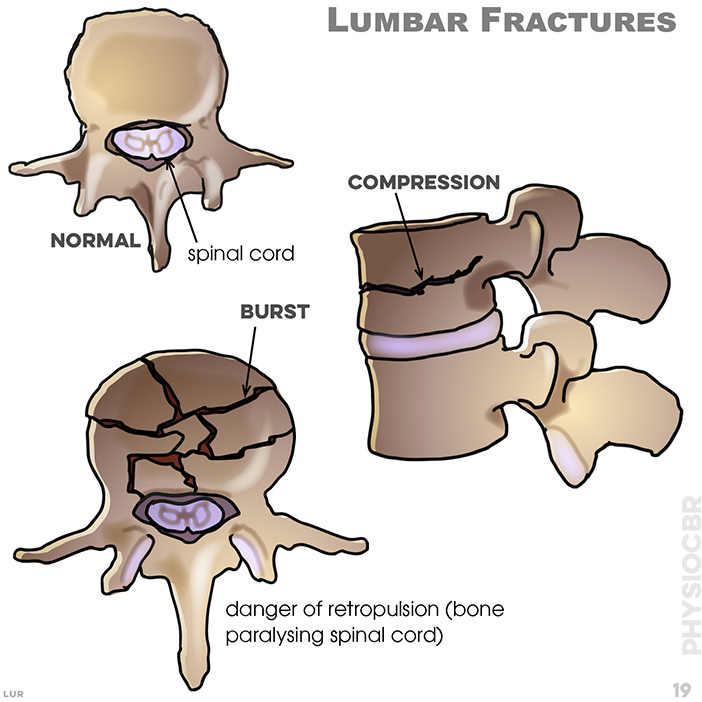
19. Lumbar fracture. trauma and spinal cord injury; trauma and spinal cord injury; compression fracture; fracture of the spinous process aithout spinal cord injury
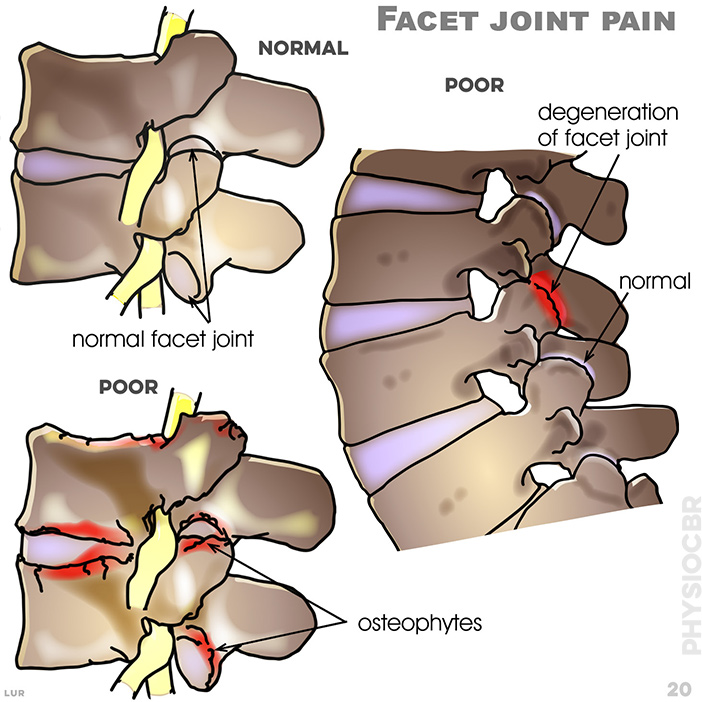
20. Facet joint pain: degeneration of facet joint; osteophytes
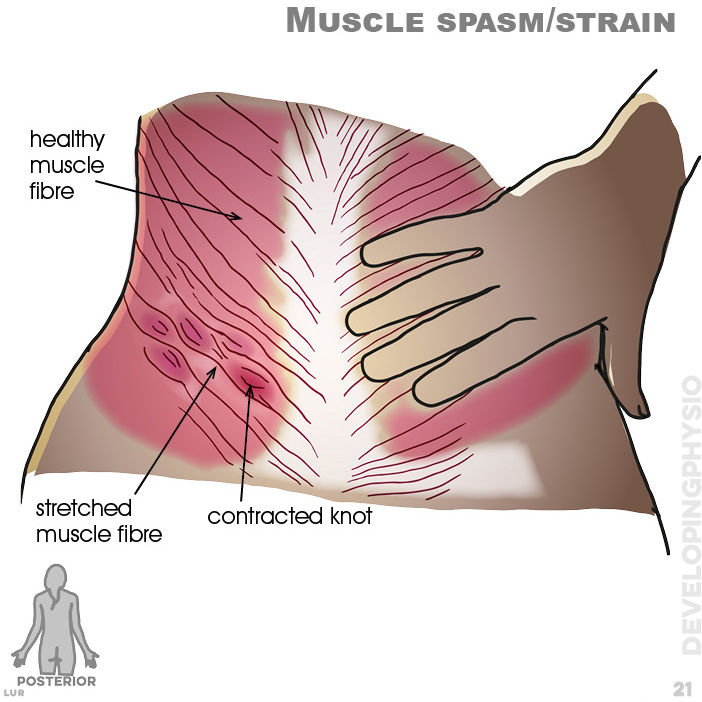
21. Muscle spasm or strain results in stretched muscle fibre and contracted knots
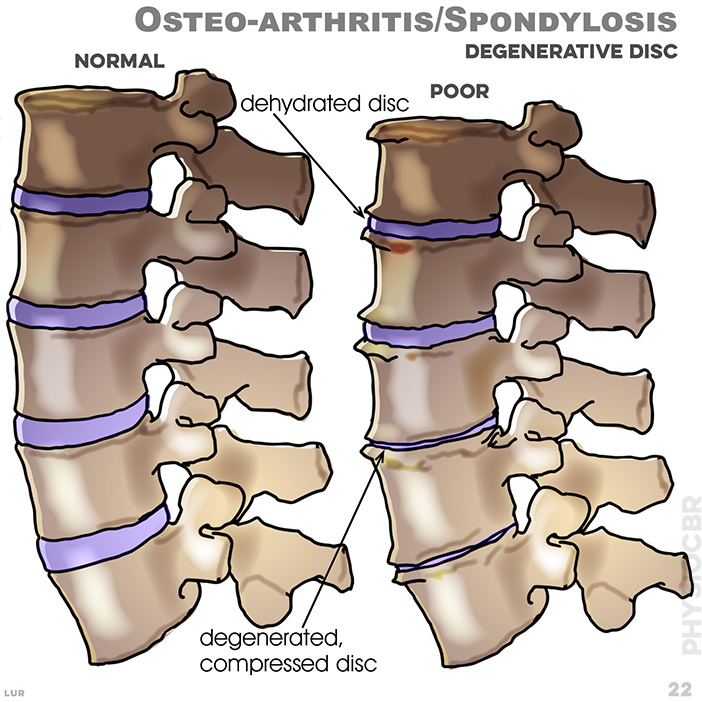
22. More common to people over 50 years, or are overweight or who have had a trauma in the past