home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides
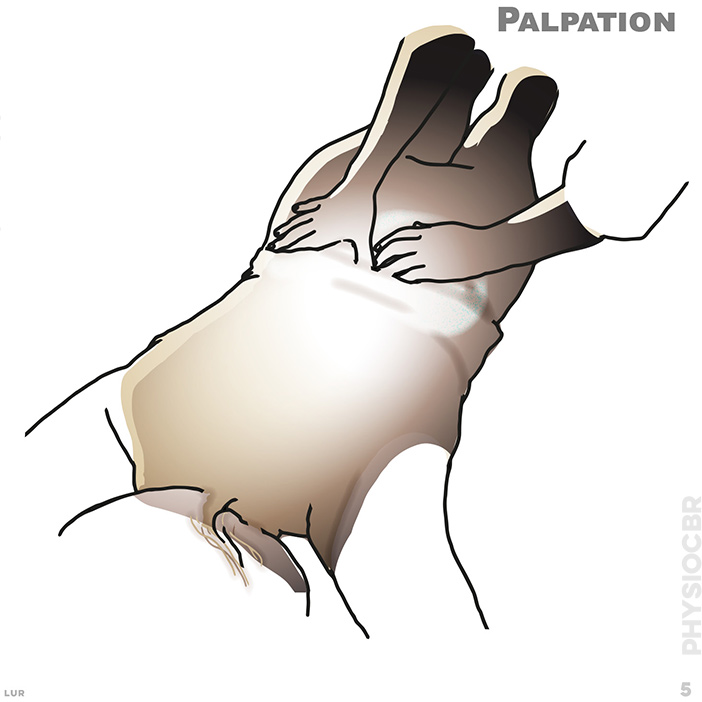
5. The lumbar palpation requires correct use of two hands on the relevant vertebrae.
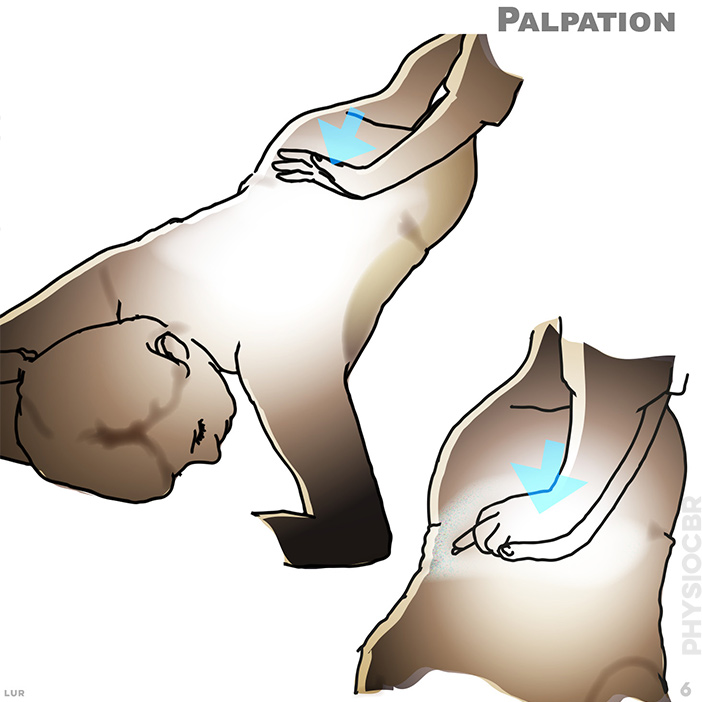
6. The side of one hand is angled fully across the relevant vertebrae. The second hand is then placed over the first to allow an even, gentle force to be applied through both arms
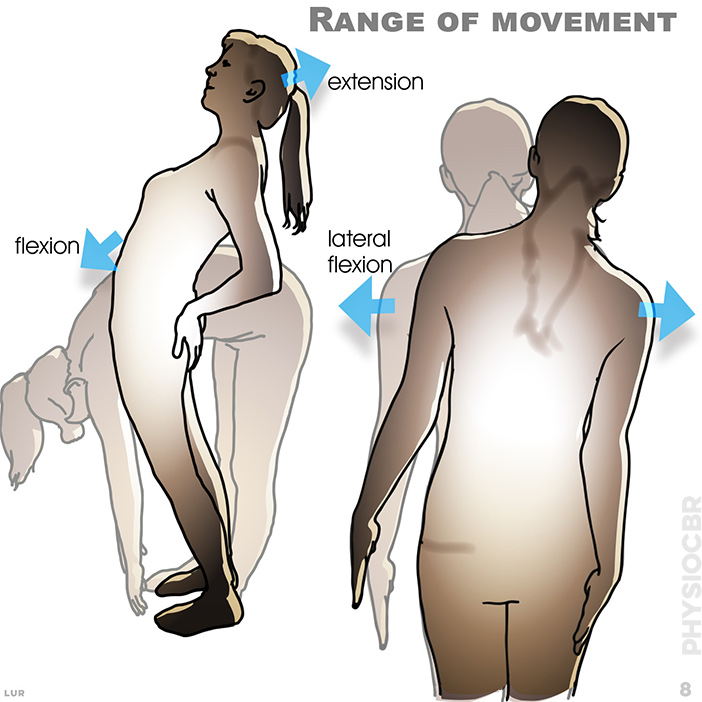
8. the sagittal plane includes extension (straightening) and flexion (bending); while the lateral plane includes abduction (moving out) and adduction (moving in)
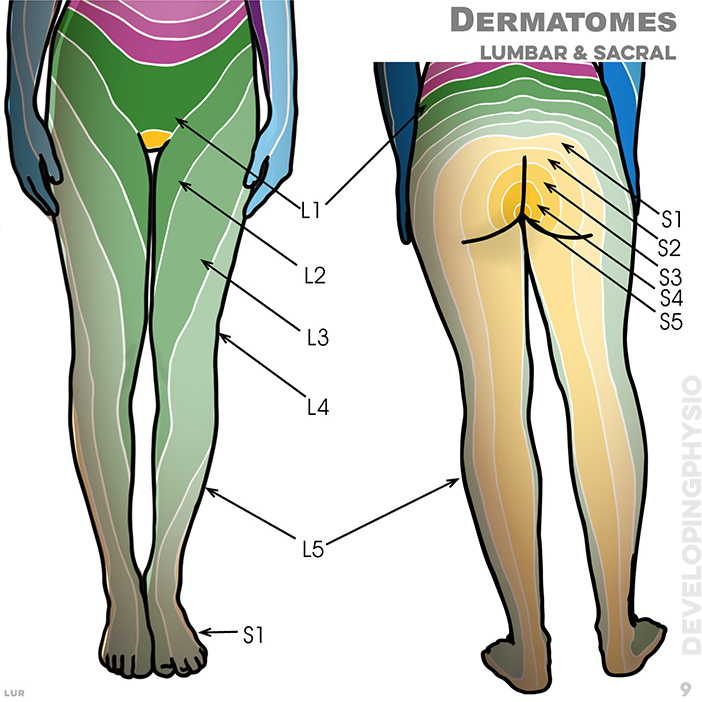
9. Dermatomes are tested by touching the skin of both legs and comparing sensation felt. A positive test is where reduced feeling is reported. Each colour relates to a single spinal nerve root.
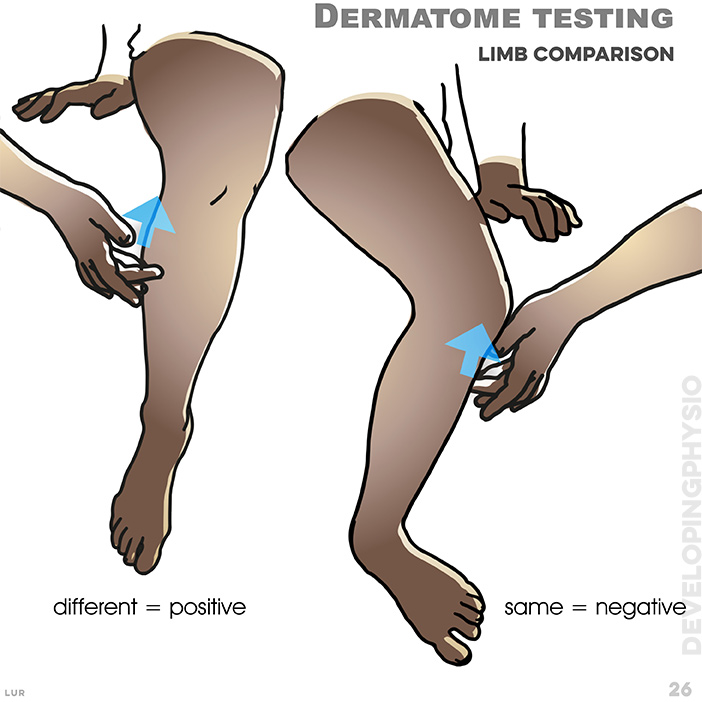
26. Compare both limbs. if the feeling is the same, then the test is negative (normal), yet if different then the test is positive
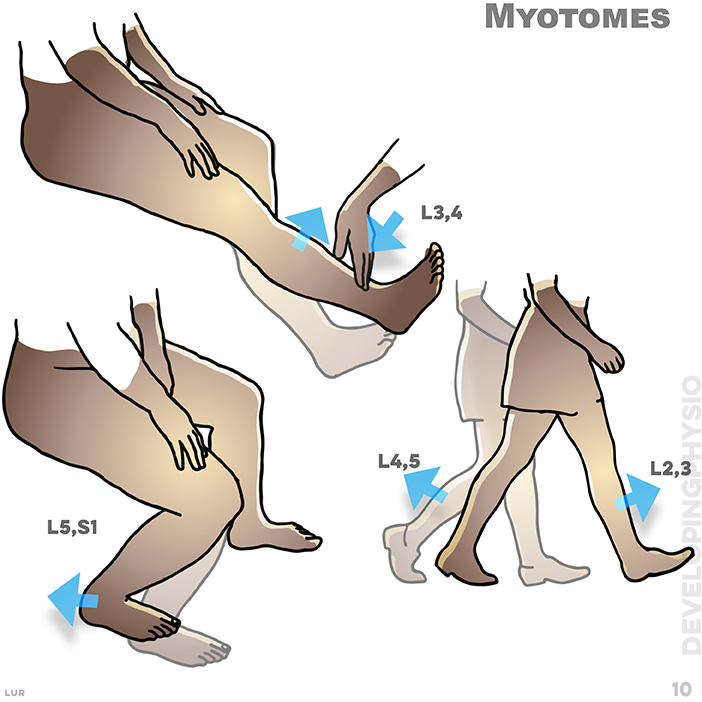
10. A myotome is the group of muscles that a single spinal nerve root supplies. If myotomes test positive, there is muscle weakness
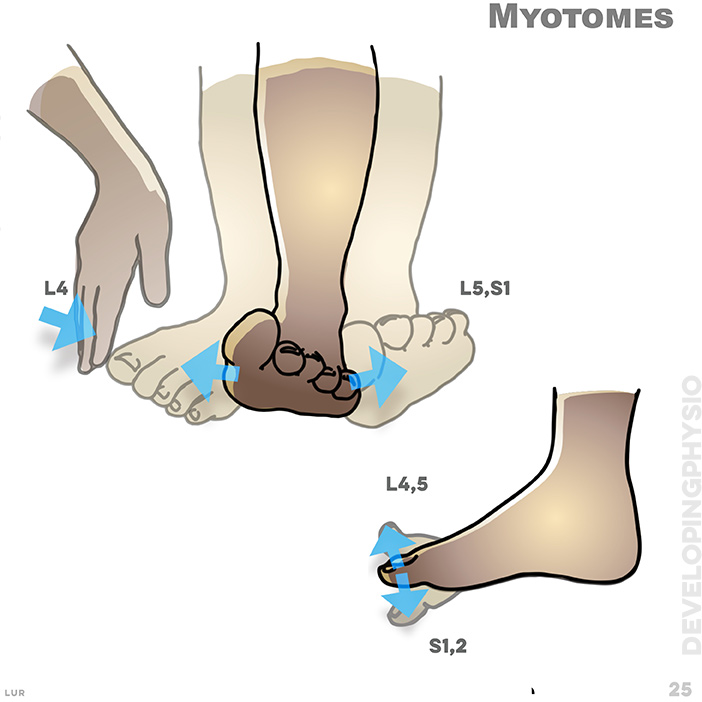
25. Myotomes. A myotome is the group of muscles that a single spinal nerve root supplies. If myotomes test positive, there is muscle weakness.
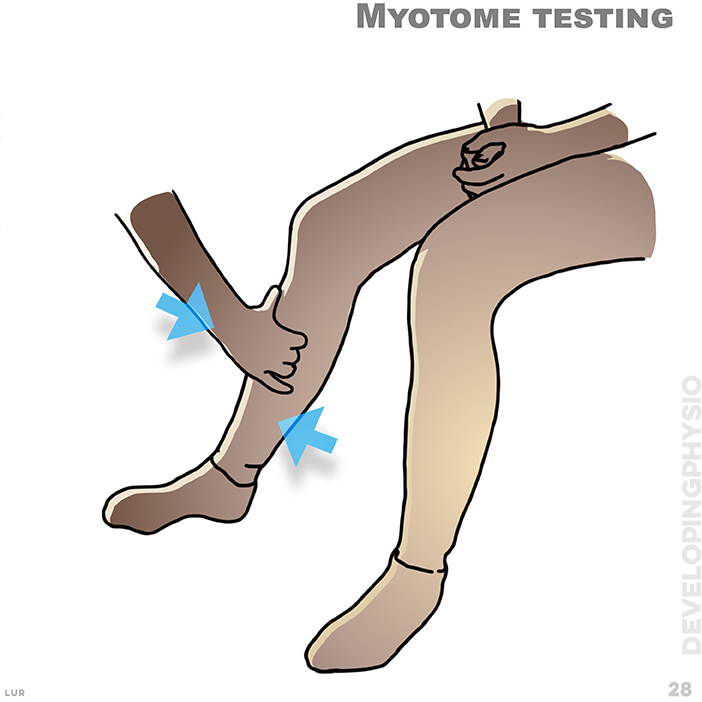
28. Myotome testing. Patient pushes against mild resistance on both legs for comparison.
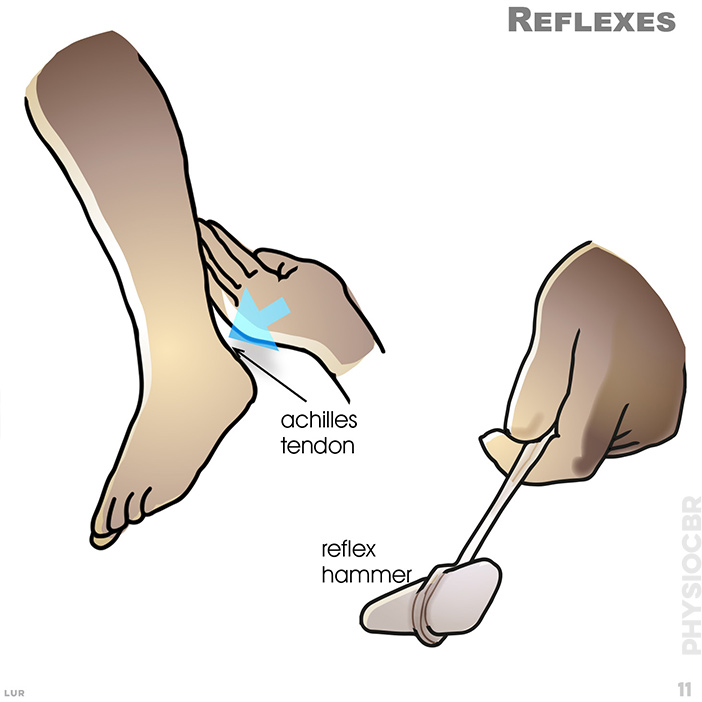
11. The knee and ankle reflexes are tested by hitting the patella and achilles tendons and observing the movement of the lower leg and foot. Slow response is a positive test, indicating a disc problem. The knee reflex is linked to the L3-L4 nerve root and the ankle to the L5-S1 nerve root. Where available, a reflex hammer is useful.
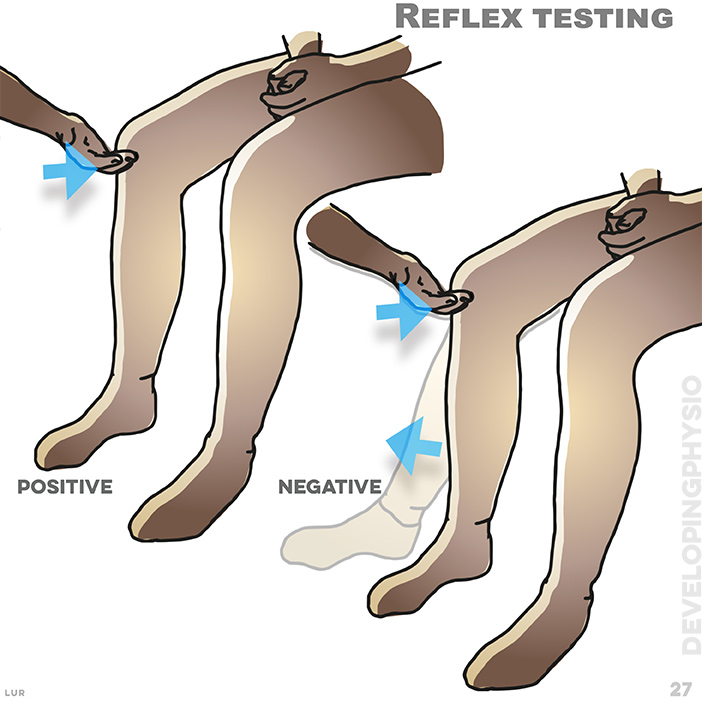
27. Knee (and ankle) reflexes are tested by hitting the tendons and observing the movement of the lower leg and foot. Slow response is a positive test, indicating a disc problem.