Glossary of terms
Common terms used by physios that are helpful to remember!
These teaching modules are for qualified physios to teach in communities who cannot access professional physio services. We do not replace such a service, but instead provide the basic skill set to reduce pain and increase function.
The respiratory module has been designed by a specialist respiratory physiotherapist and proofed by a core team of physios specialising in rehabilitation for Lower and Middle Income Countries (LMIC). As with other DevelopingPhysio modules, considerable emphasis is placed on images to encourage understanding, thereby reducing the need for literacy and translations. Each image is captioned to allow for its translation (and see below).
This module is designed for appointed community workers (who, as students, do not require any medical background). Tests are included to allow the teaching physio to check their student's understanding and progress. Eventually, the trained community worker is able to assess, diagnose and treat patients within their community.
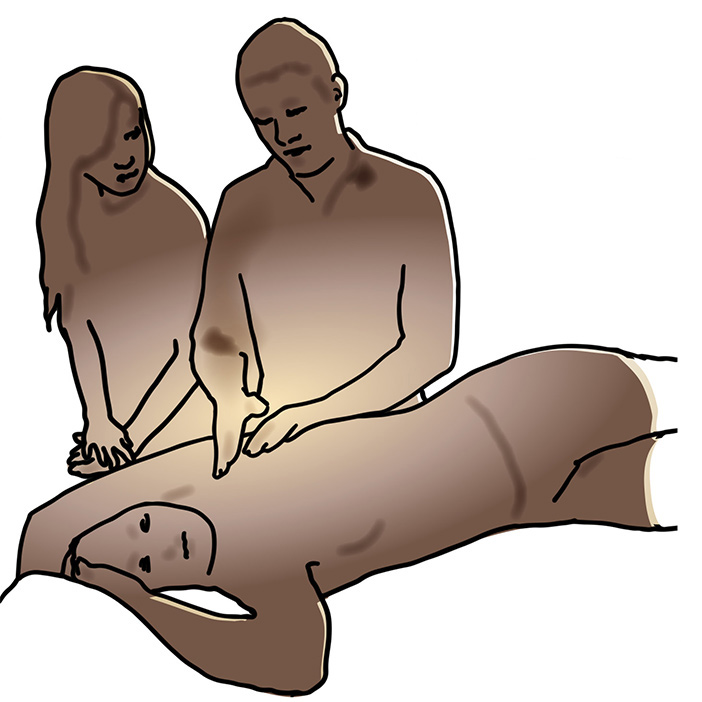
The module can be printed out, although for a better learning experience and environmental reasons, we strongly recommend online use!
Before teaching begins, this preliminary check is taken by the student to ascertain any background knowledge. This test is repeated after their exam stage, to indicate improvement and grow confidence.
(more of these quizzes are in preparation)
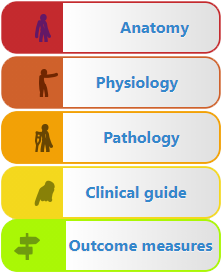
The first section is in the form of a library, that provides specific information on relevant Anatomy, Physiology and Pathology
This is followed by a Clinical guide which introduces the Objective assessment in an intuitive way to help the teaching physio demonstrate how clinical reasoning works and how a diagnosis will be made. Finally, Outcome measures determine the ongoing improvement of the patient.
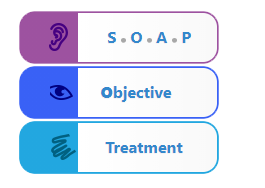
This section introduces the logic of SOAP
(Subjective, Objective, Analysis
& Plan)
Within this framework, the Objective section provides an intuitive picture flow sequence to prompt
the user through the critical tests that determine
the diagnosis of the patient, which in turn leads to their recommended Treatment.
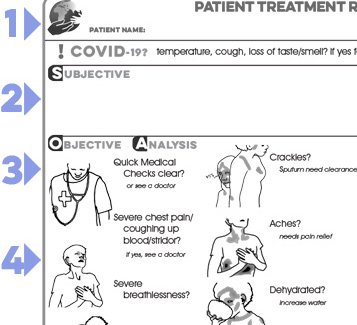
Patient notes are a legal requirement and very important to maintain correctly. They follow the S.O.A.P. protocol and a quick explanation of this is provided
We recommend an exam after the teaching to assess whether the student is safe to assess, diagnose and treat patients. See more information
Now you have taught the module, repeat the pre/post learning test and your student will see their higher score.

The module finishes with a resources section where teachers and students can find further reading, learning games and students tests

Your feedback is vital in helping us refine the module for the benefit of all users, so please dont hesitate to give us your thoughts!
This 'red flag' icon indicates "See a doctor!" Where no doctor exists, then please take any practical medical alternative action possible.
For translation needs, Google Chrome is the recommended browser, since it provides the simplest means to convert text into another language. However, as it will only work with internet connected, we are keeping an eye on Firefox who are developing an offline translation service.

To use this module without internet connection, click the small download button at the top right of your screen (whilst online). You will then be taken through a very quick app installation process so that an icon can then be installed the homescreen of your device. Pages you visit whilst online are then cached (automatically stored) and any updates to the module will automatically occur when you are next online.

The possibility for further learning resources for online classes that include tests, games and module examination to help determine when a student is ready to work independently with patients, is being looked into via an online Learning Management System (LMS). This in turn would affect funding and possible progression to the future teaching of more physios. Please let us know if this subject interests you!