home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides

12. Soft tissue healing. Acute inflammation blood clot forms, tissue disruption. 72 hours. Regeneration clot shrinks, new fibrous tissue forms. 72 hours – 6/8 weeks. Re-modelling tissue fibres become organised. 6/8 weeks – 6/12 months.
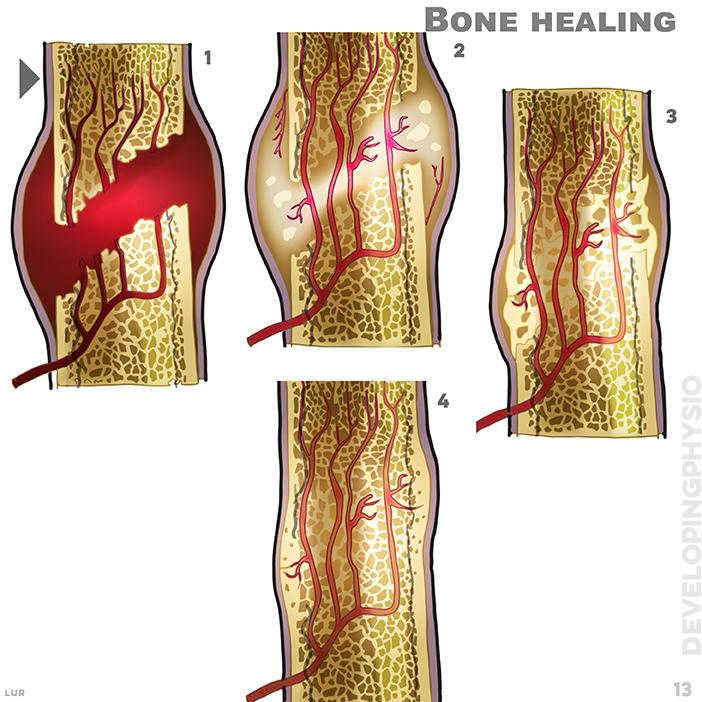
13. Bone healing: haematoma, week 1. soft callus, week 2 to 3. hard callus weeks 4 to 16. remodelling week 17 onwards
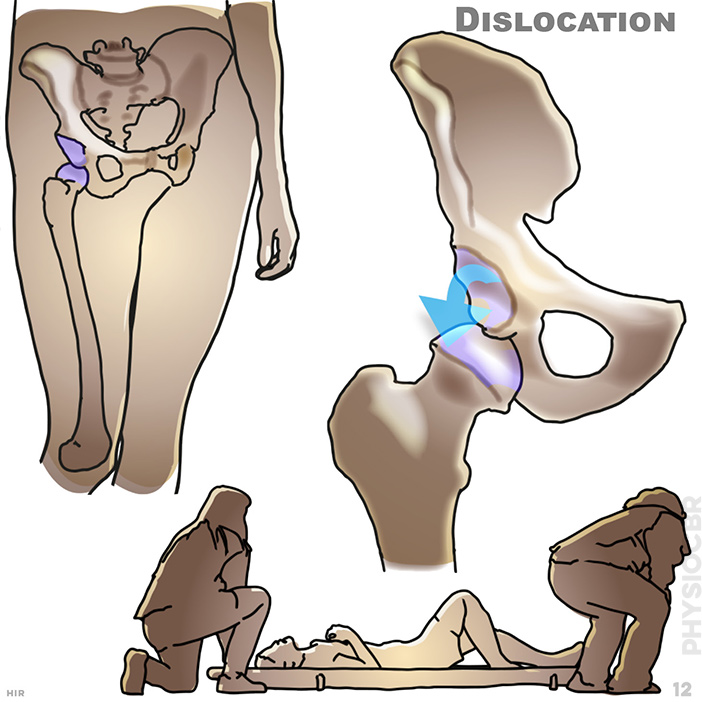
12. Dislocation: If possible seek medical assessment

13. Fractures: Fractures can result from a fall, direct trauma, or being involved in a road traffic accident. If possible seek medical assessment
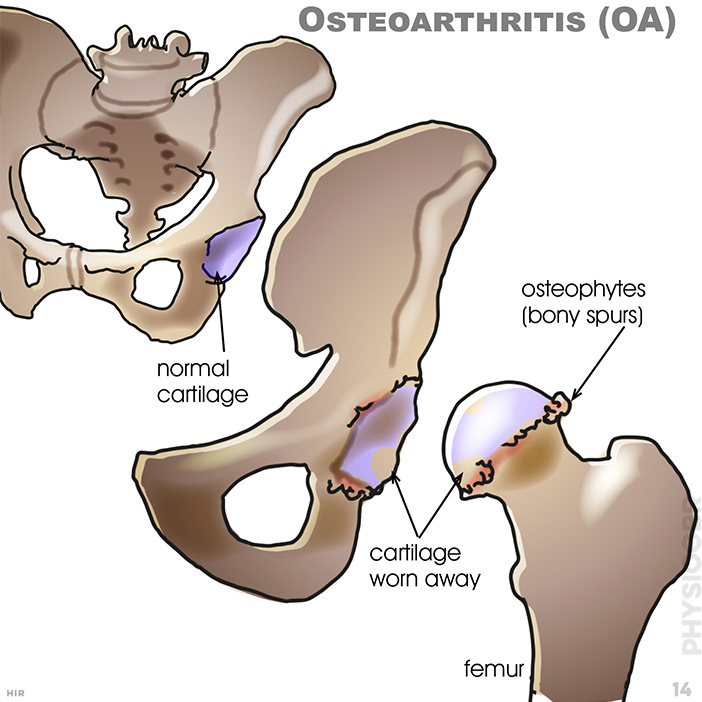
14. Osteoarthritis (OA): Joint cartilage helps to protect the joint from load;normal cartilage, osteophytes (bony spurs); cartilage worn away; femur
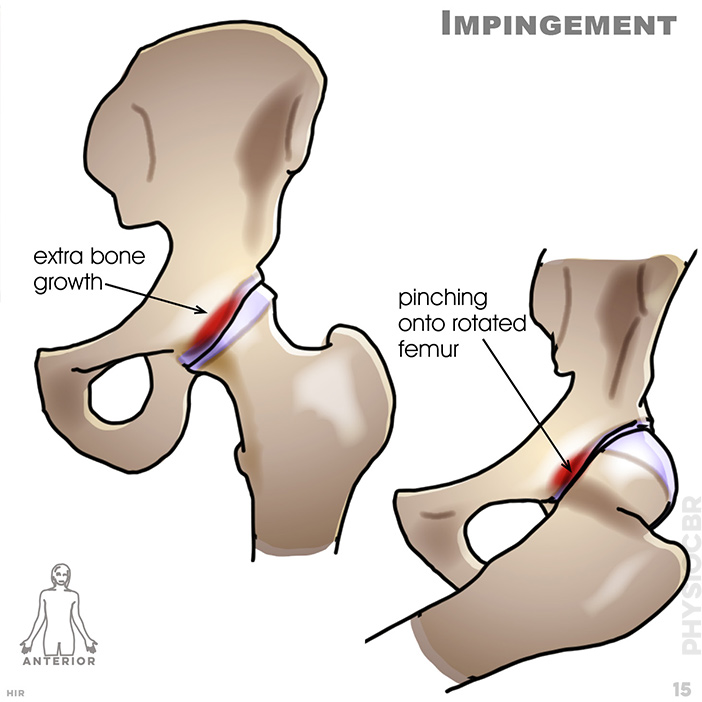
15. Impingement: extra bone growth; pinching onto rotated femur
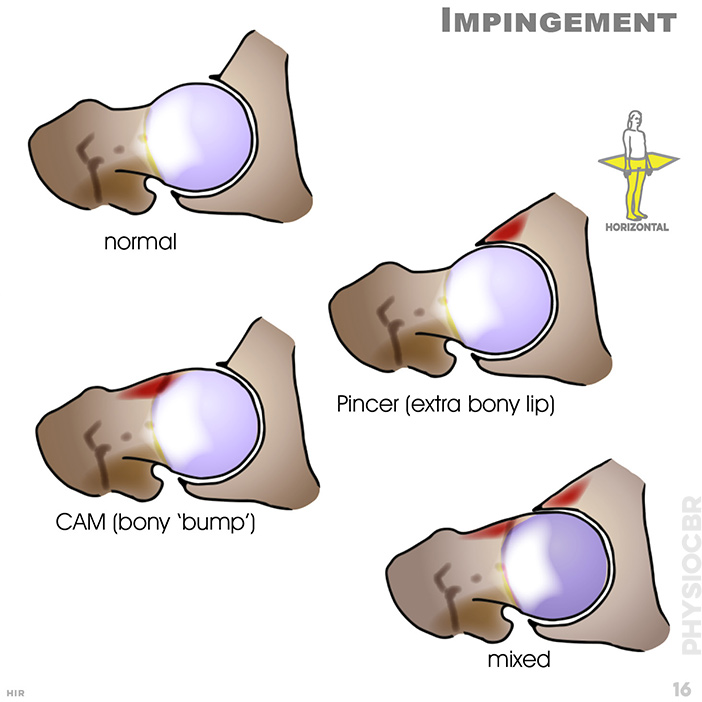
16. Impingement: normal; pincer (extra bony lip); CAM (bony 'bump'); mixed
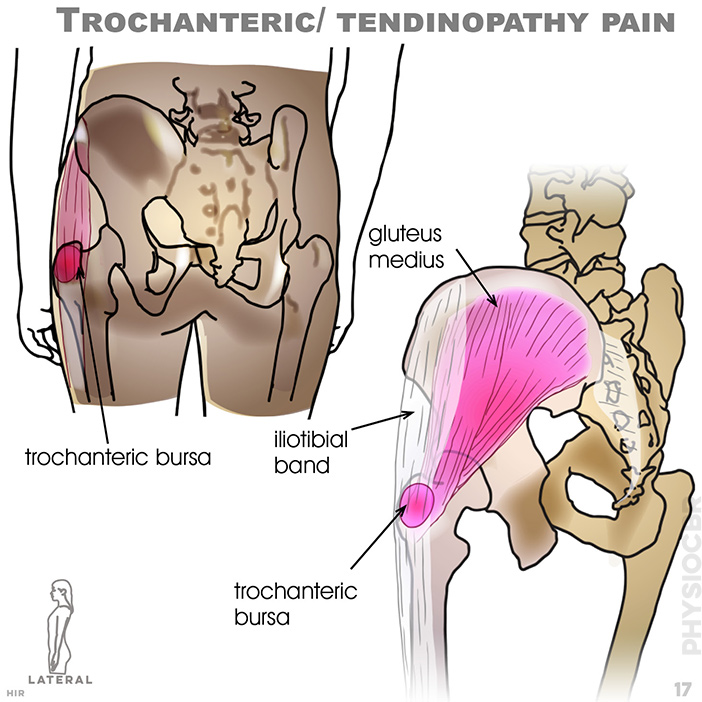
17. Trochanteric/ tendinopathy pain : Gluteal tendinopathy/trochanteric bursitis; gluteus medius; trochanteric bursa; iliotibial band; trochanteric bursa
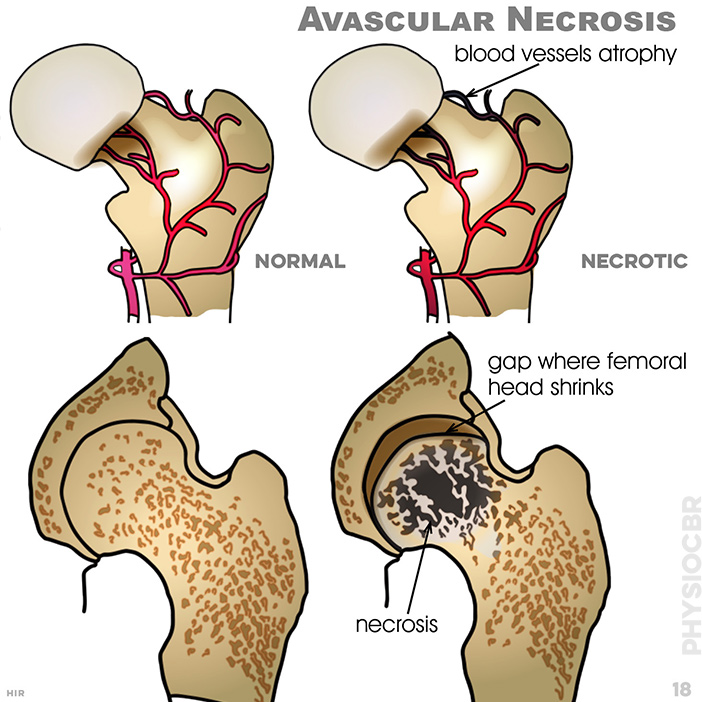
18. Avascular Necrosis: blood vessels atrophy; gap where femoral head shrinks; necrosis
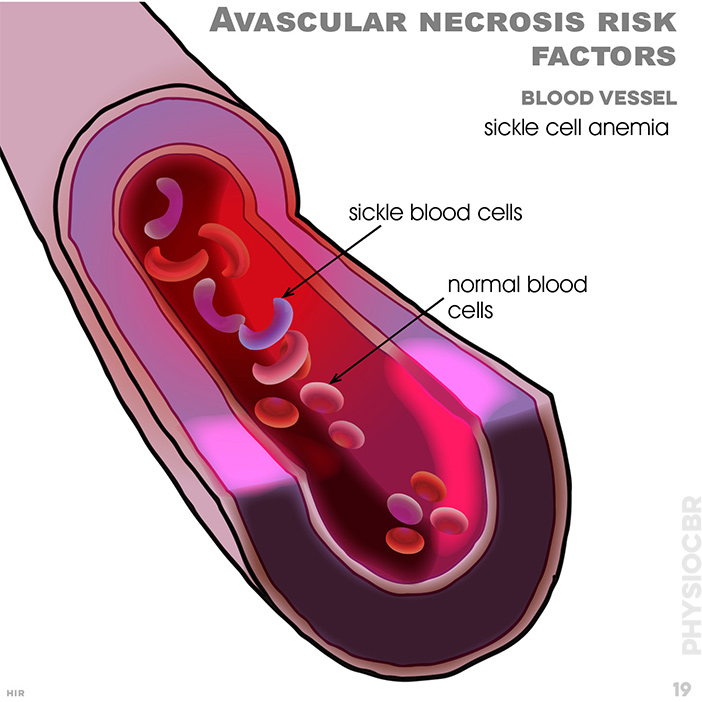
19. Avascular necrosis risk factors: blood vessel; sickle cell anaemia; sickle blood cells; normal blood cells
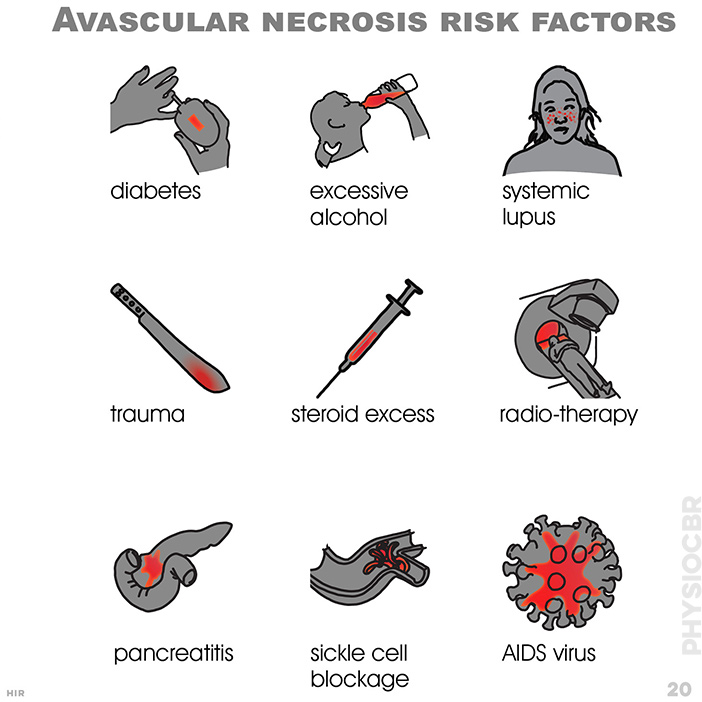
20. Avascular necrosis risk factors: diabetes; excessive alcohl; systemic lupus; trauma; steroid excess; radiotherapy; pancreatitis; sickle cell blockage; AIDS virus/p>
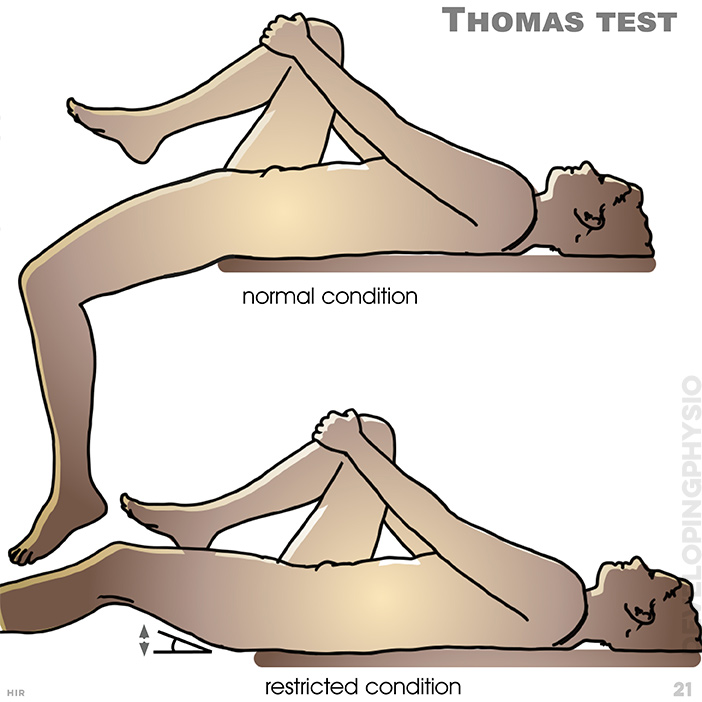
21. Thomas test: Test the rectus femoris muscle which may be restricted, preventing flattening of leg. (hold knee to chest and let other leg hang over bed, while lying back on bed)
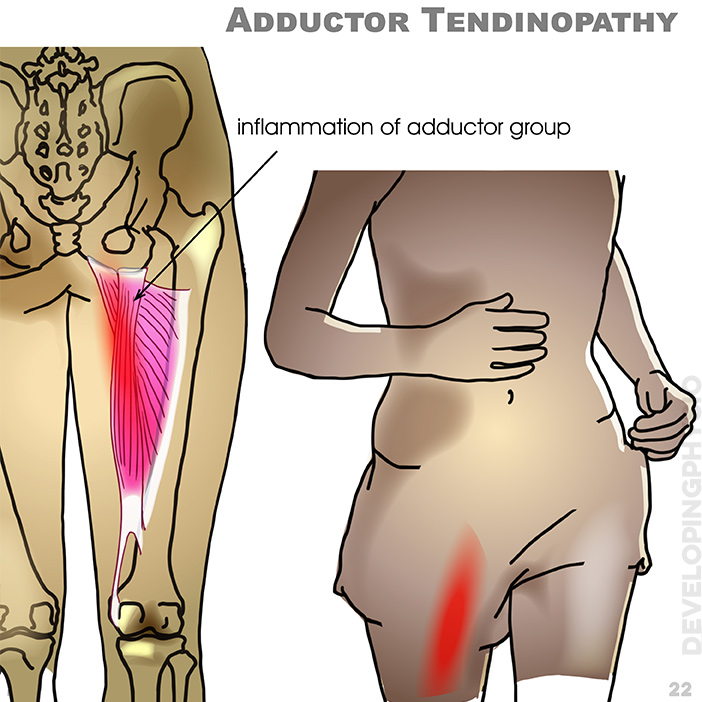
22. Adductor Tendinopathy: inflammation of adductor group