Pathology
home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides
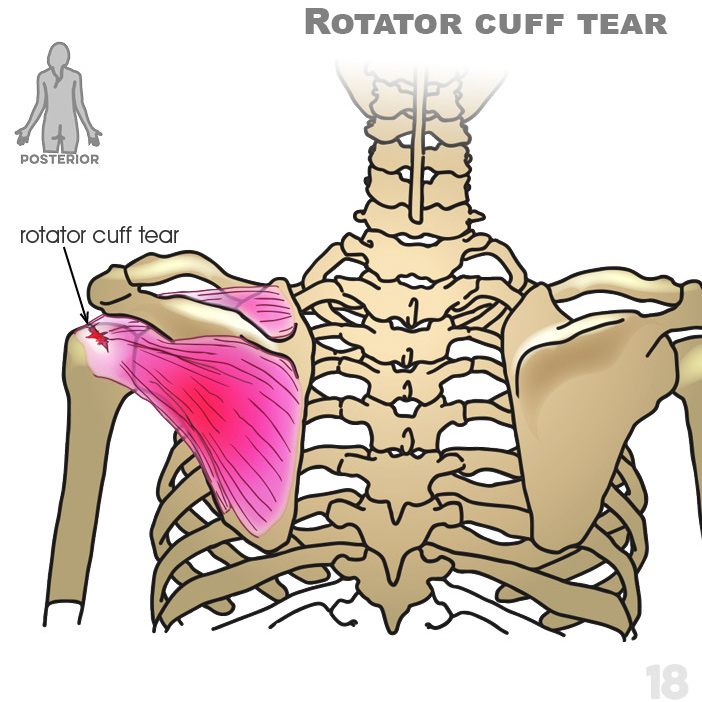
18. Rotator cuff tear
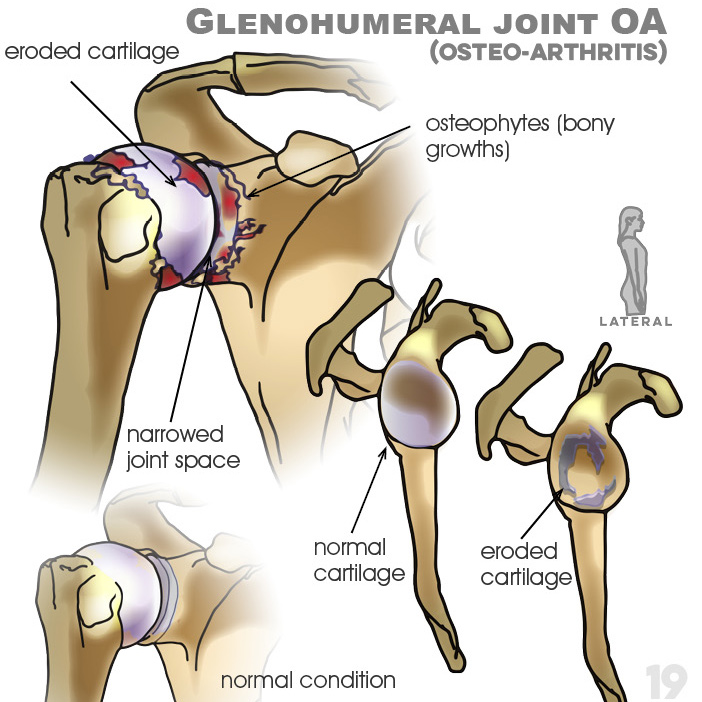
19. Glenohumeral joint OA (osteoarthritis): osteophytes (bony growths), eroded and normal cartilage, narrowed joint space. OA can also happen after trauma
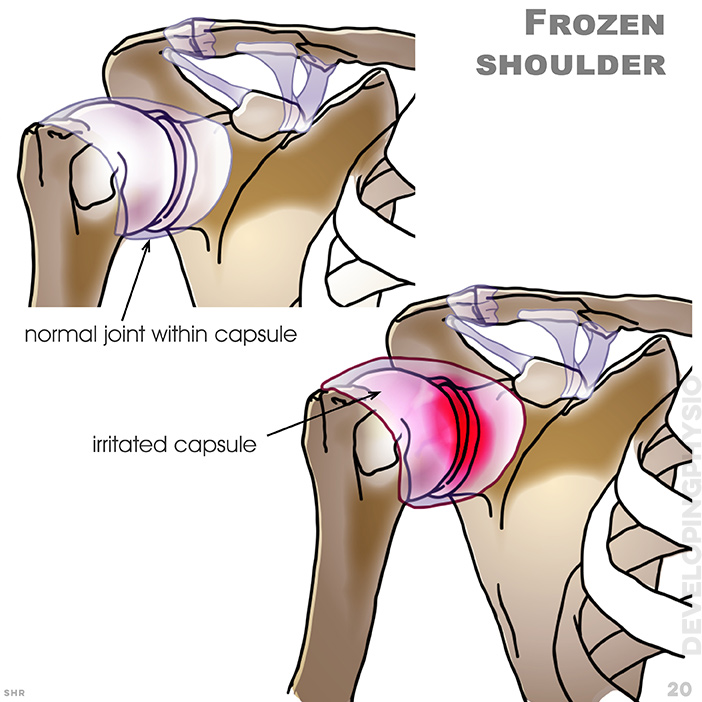
20. Frozen shoulder: Occurs when the flexible tissue surrounding the shoulder, the capsule, becomes inflamed and thickened, leading to the reduction of movement, normal joint within capsule, irritated capsule
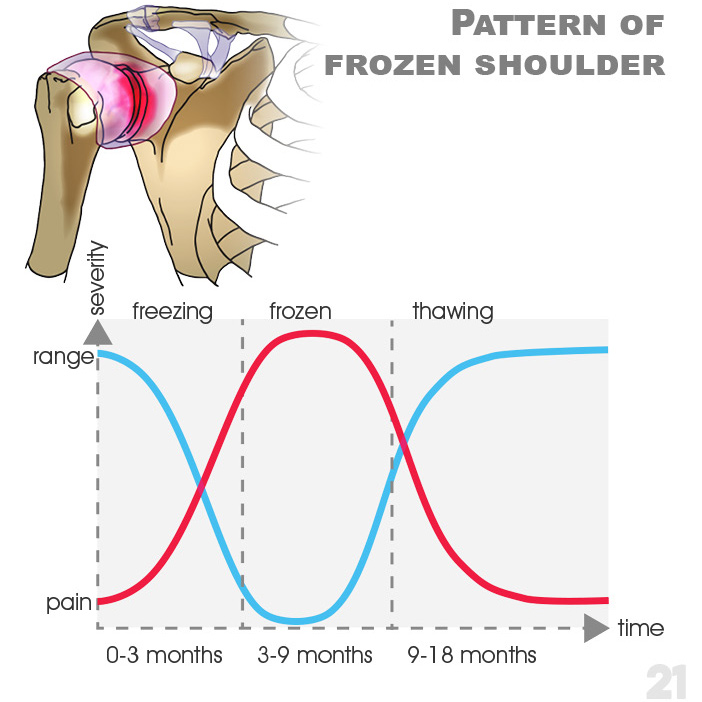
21. Pattern of frozen shoulder: freezing/ frozen/ thawing. severity; range/ pain; time
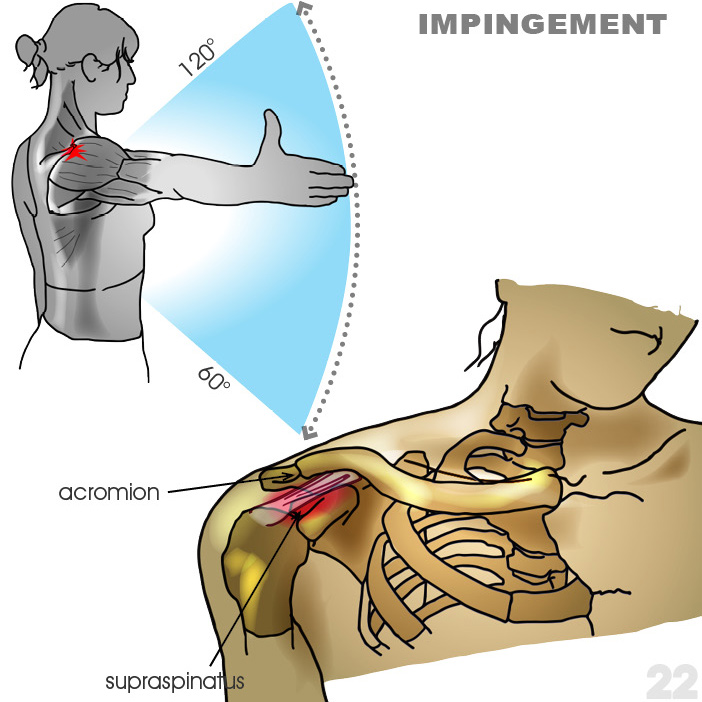
22. Impingement: Irritation to structures located below the edge of the acromium can lead to pain, often referred to as impingement. Impingement is most common between the degrees shown.
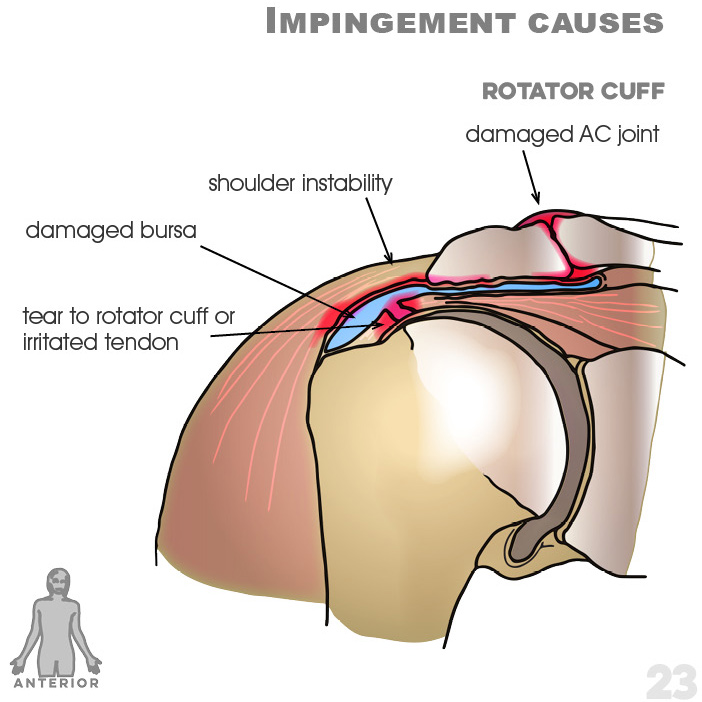
23. Impingement causes: damaged AC joint, shoulder instability, damaged bursa, tear to rotator cuff or irritated tendon
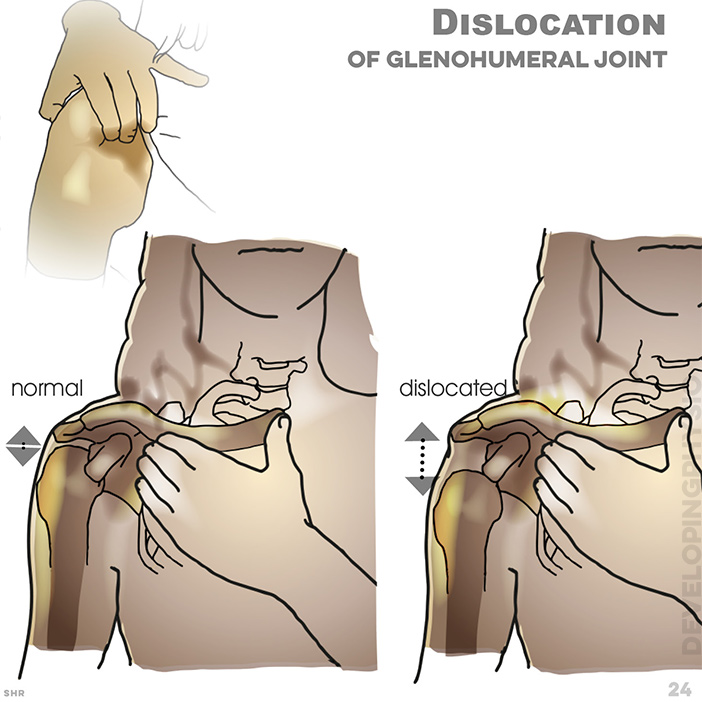
24. Dislocation of glenohumeral joint
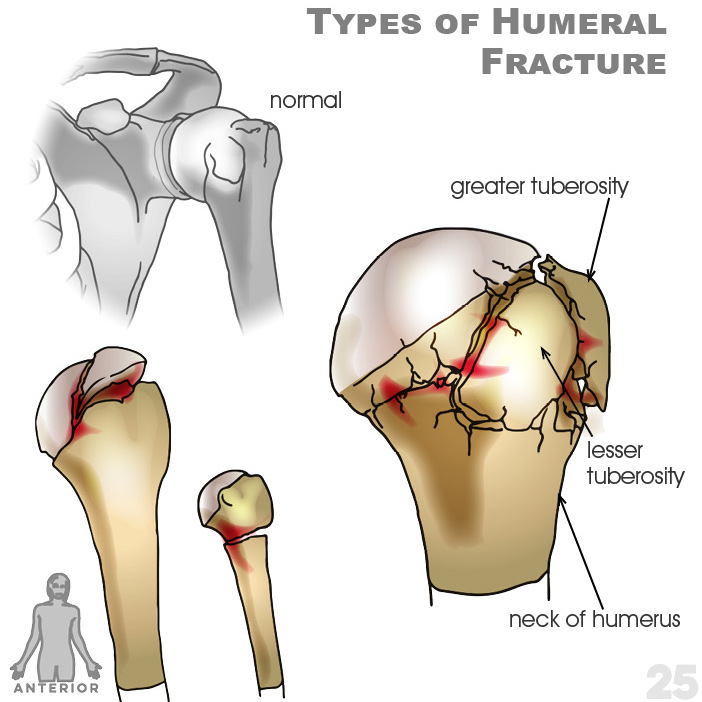
25. Types of Humeral Fracture: greater and lesser tuberosity, neck of humerus
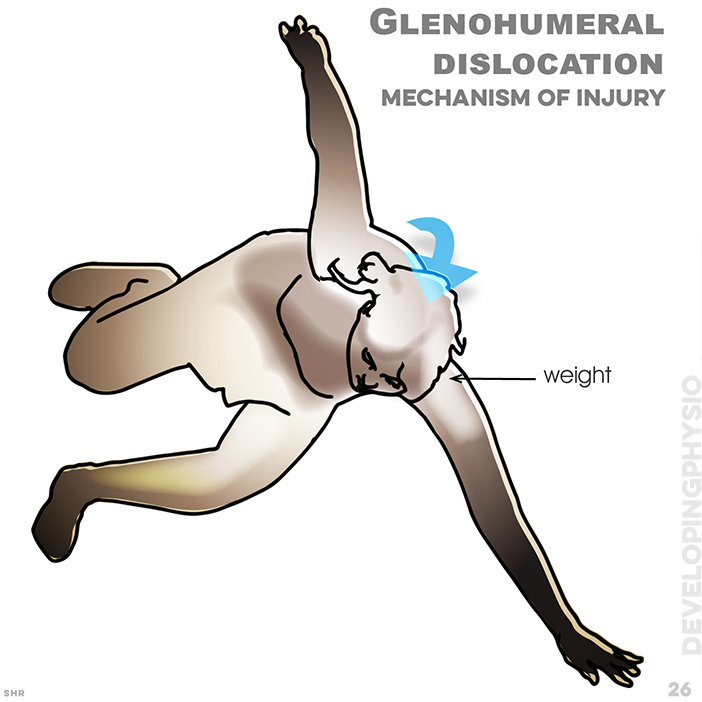
26. Glenohumeral dislocation: Most commonly dislocation injuries are from a fall onto an outstretched arm, when weight on impact is transferred to joint
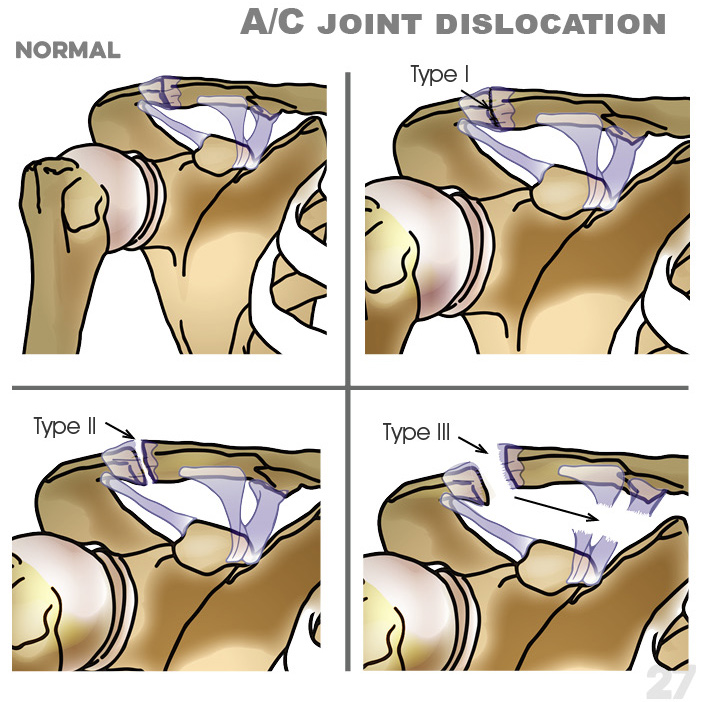
27. A/C Joint dislocation
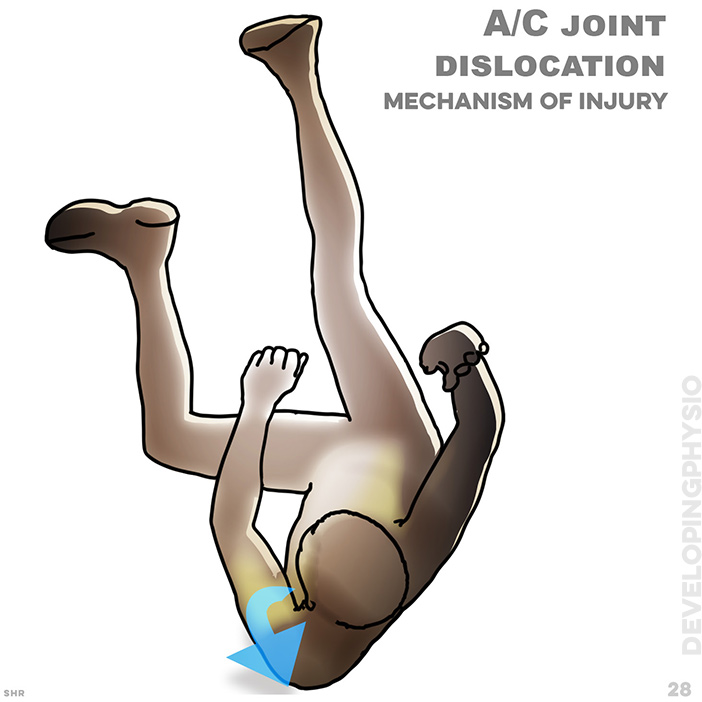
28. A/C Joint dislocation, mechanism of injury: Most commonly from a fall directly onto shoulder with arm adducted. Or through being hit on outside of shoulder
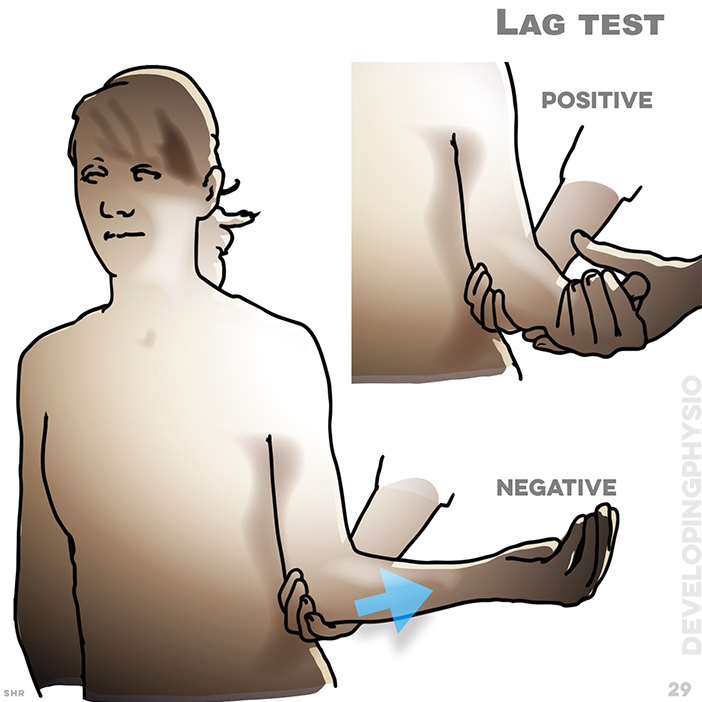
29. Lag test: Passively rotate the patient’s arm into full external rotation. negative result means patient can maintain this position without aid; positive result means patient cannot maintain full rotation without aid