home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides
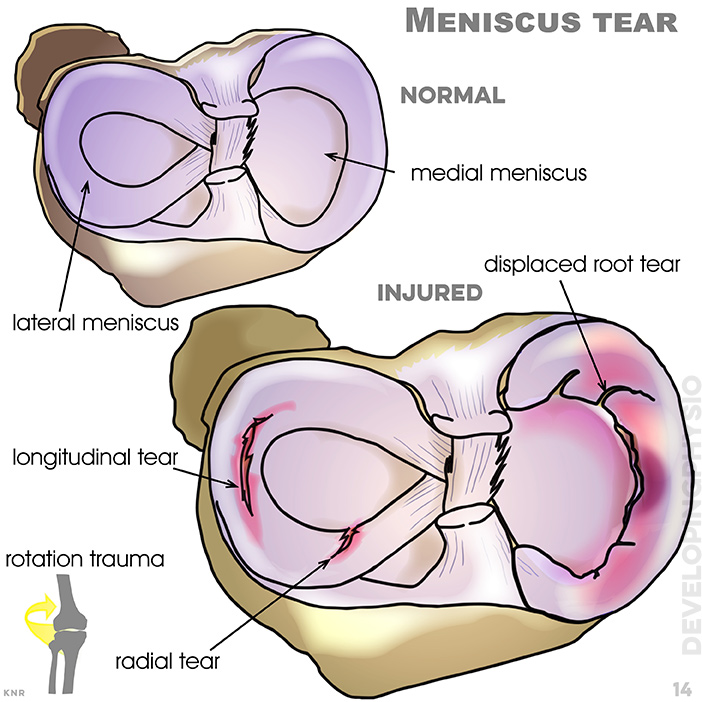
14. Meniscus tear: Injury usually occurs after a trauma, although in elderly patients it can occur spontaneously, causing swelling and bruising
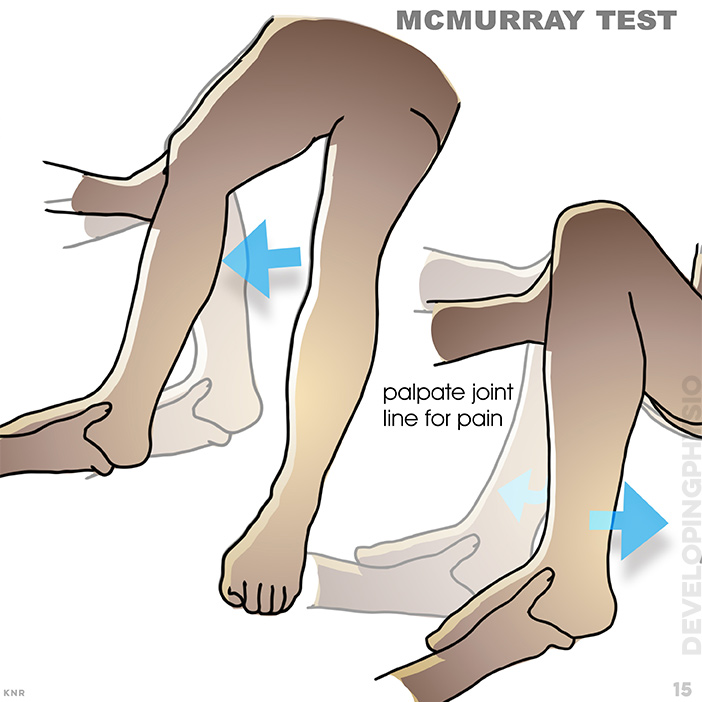
15. McMurray test: Meniscal test. A positive test replicates the patient’s pain and there can also be an evident clunk/click
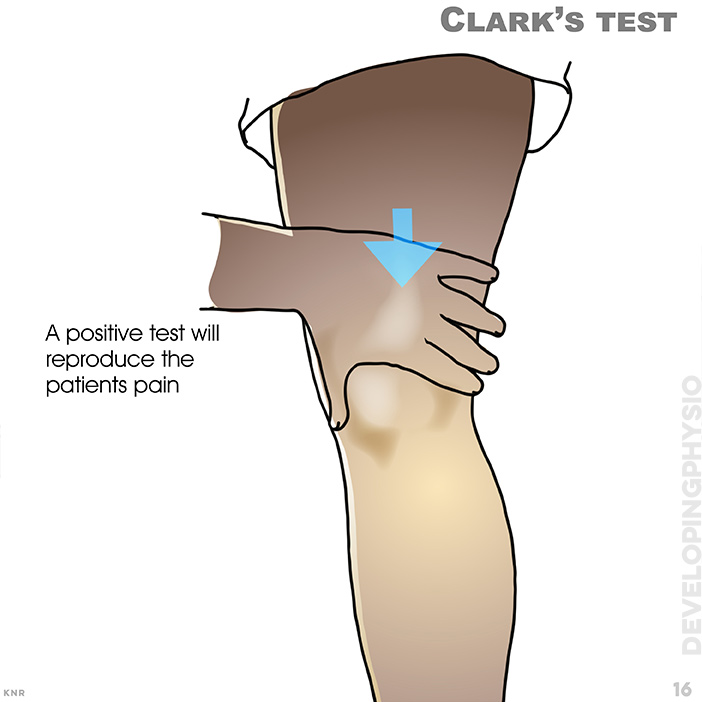
16. Clark’s test: For problem between patella and femur. Apply pressure just above the patella and ask the patient to gently and gradually contract their thigh muscles (straighten the knee more). A positive test is pain underneath the patella
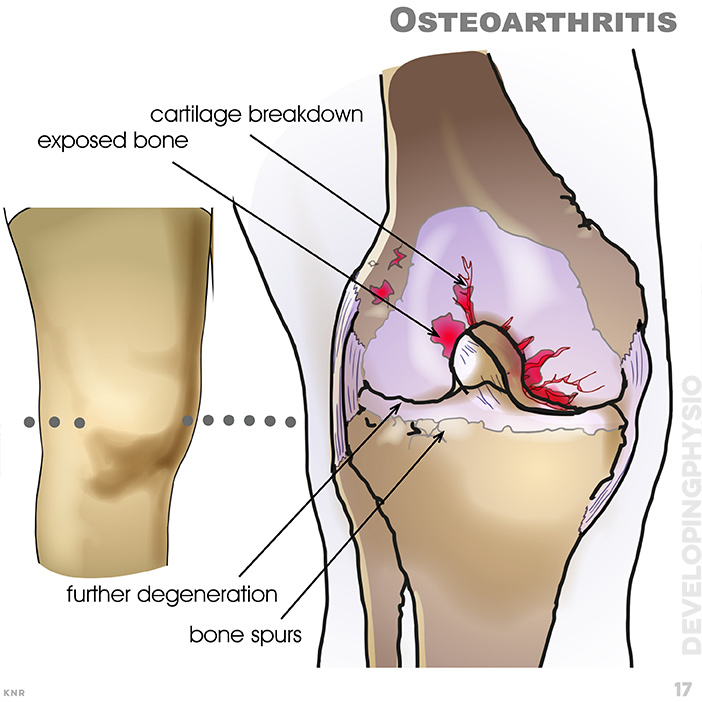
17. Osteoarthritis: Degenerative condition in over 50 years olds. Cartilage is connective tissue and has no nerve supply so pain cannot be felt easily, yet usually occurs after too long rest, or when starting activities. The is usually knee slightly swollen (often on both sides) and joint line is painful to palpate
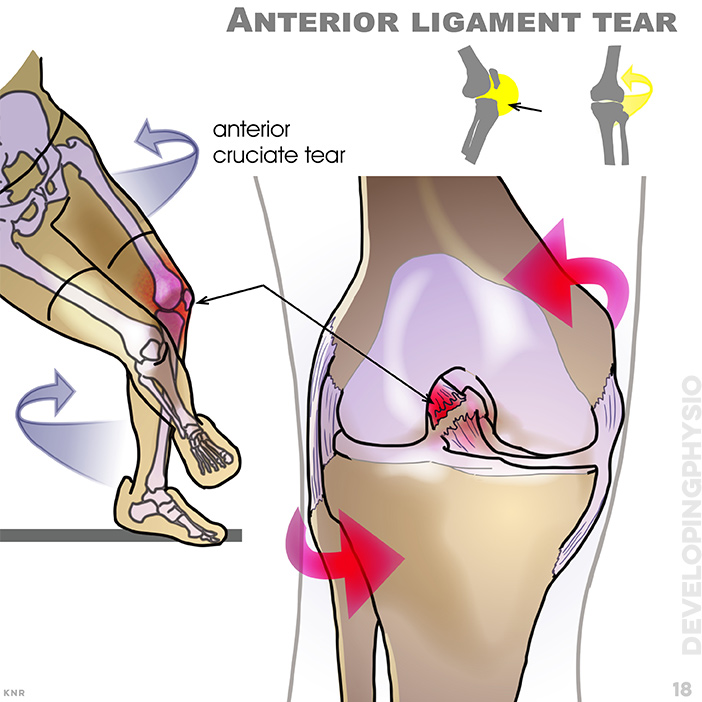
18. Anterior ligament tear: Caused by excessive rotation, often in combination with tear to meniscus and medial collateral ligament (refer to anterior drawer test)
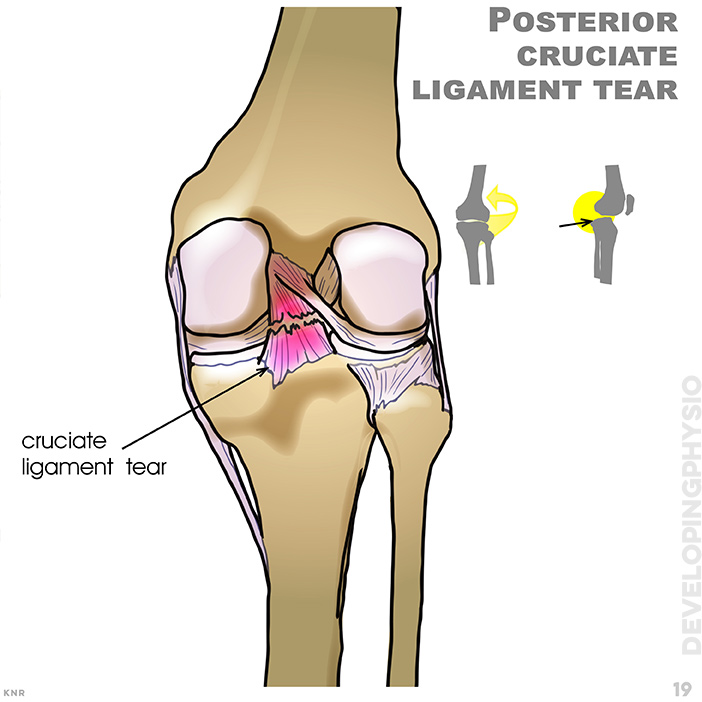
19. Posterior cruciate ligament tear: Caused by excessive rotation or when lower leg is forcefully pushed back in relation to the upper leg. Occurs less often than anterior cruciate ligament tear. (refer to posterior drawer test)
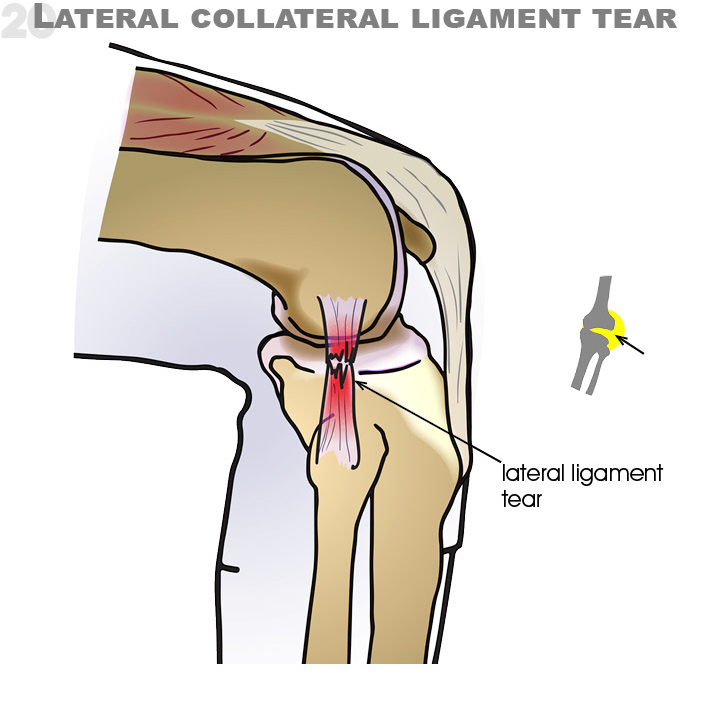
20. Lateral collateral ligament tear: When lower leg is forced to the inside (adduction) Often when knee is in flexed position. (refer to Varus test)
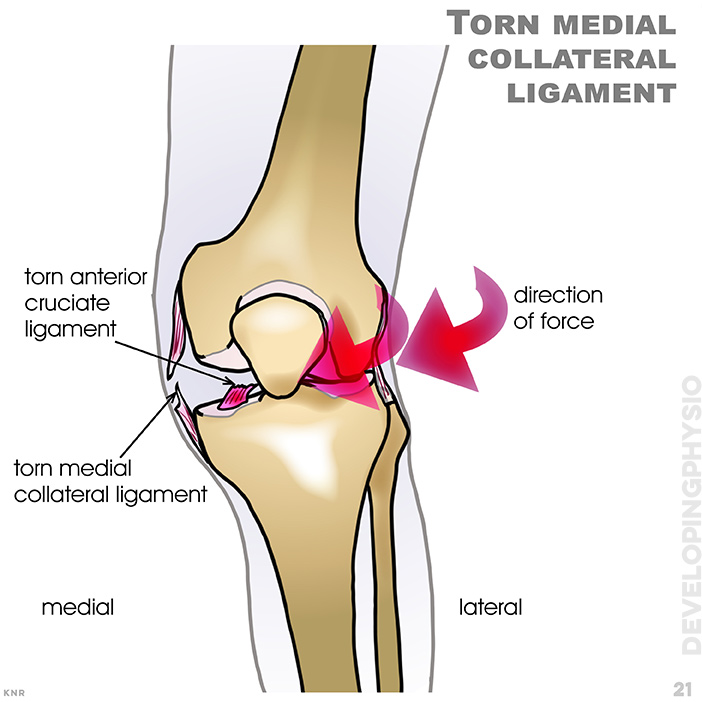
21. Torn medial collateral ligament: When lower leg is forced to the outside (abduction) often when knee is in flexed position (refer to Valgus test)
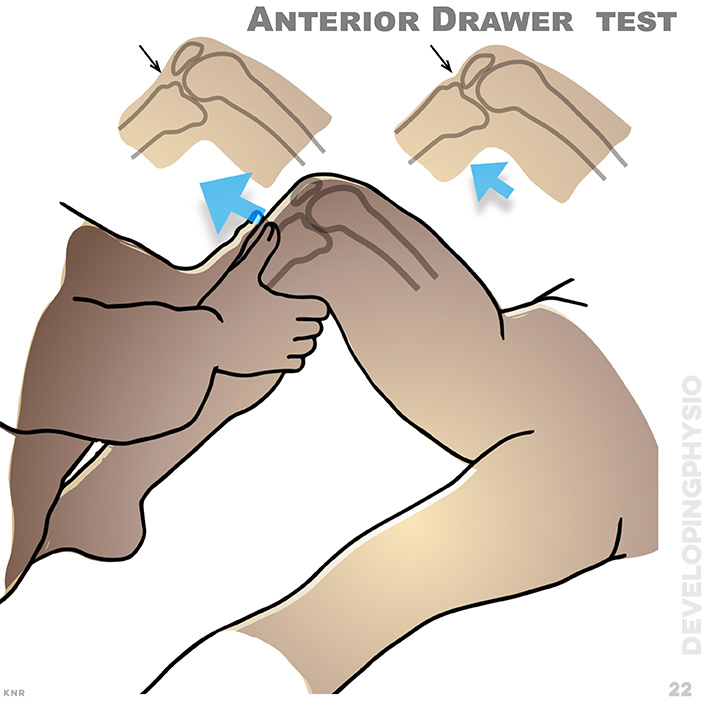
22. Anterior Drawer test: Anterior cruciate ligament test for joint laxity. A positive test is increased movement without an obvious springy block (end-feel))
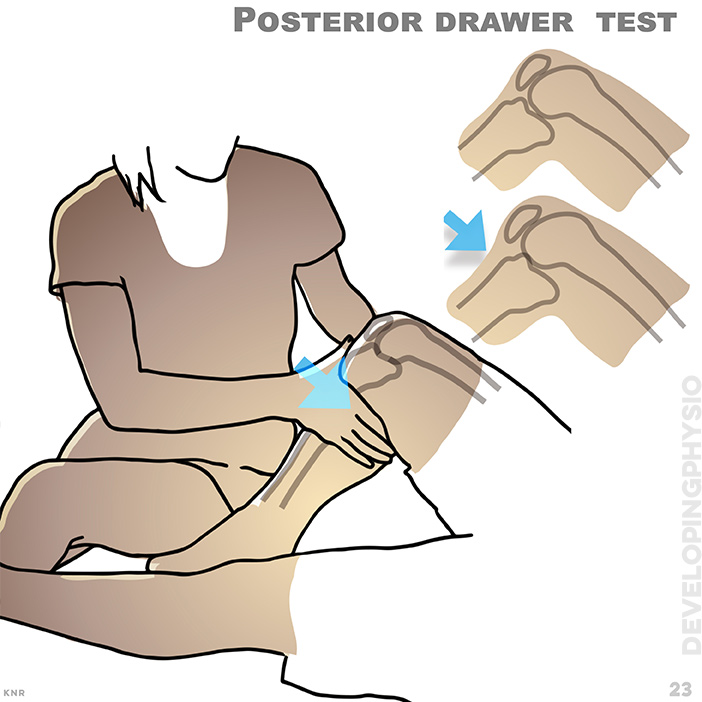
23. Posterior drawer test: Posterior cruciate ligament test for joint laxity. A positive test is increased movement without an obvious springy block (end-feel)
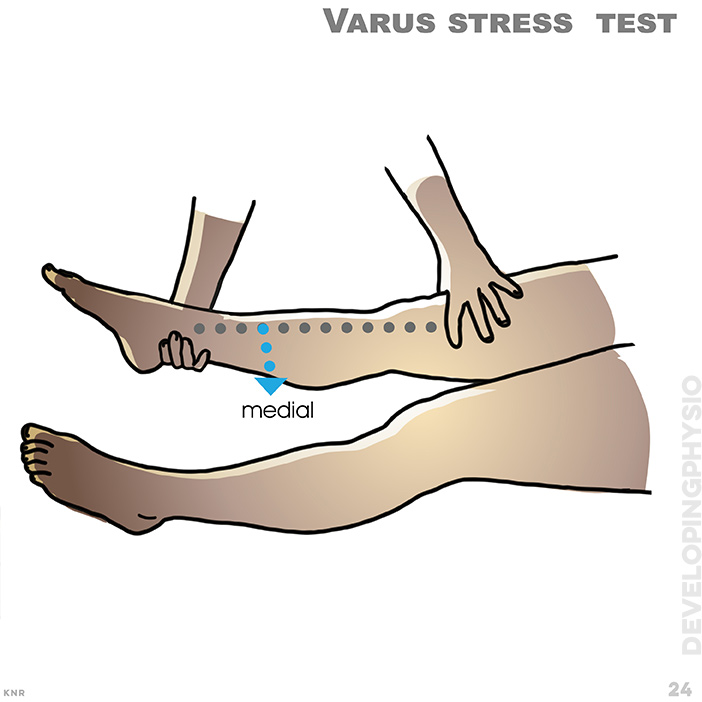
24. Varus stress test: Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) test. A positive test is increased movement without a obvious springy block (end-feel)
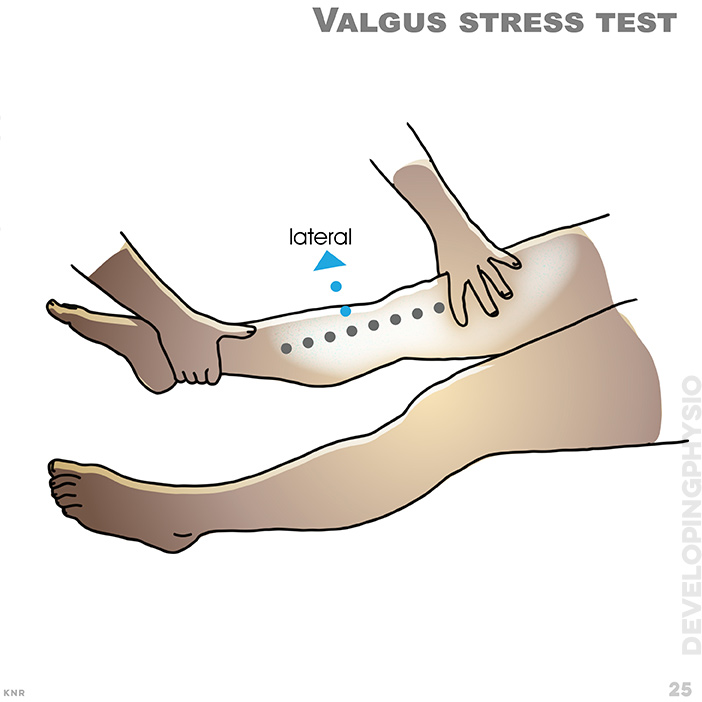
25. Valgus stress test: Medial collateral ligament (MCL) test. A positive test is increased movement without a obvious springy block (end-feel)
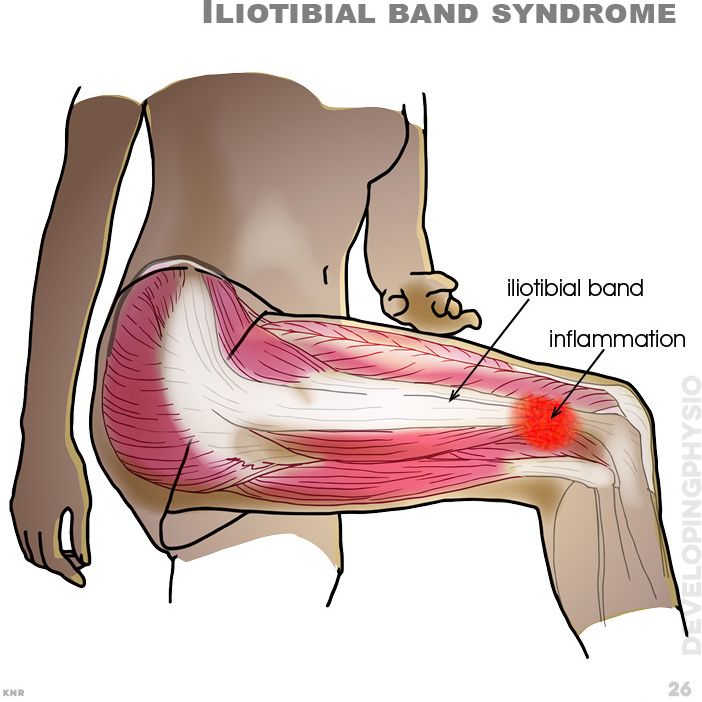
26. Iliotibial band syndrome: ITB syndrome is an overuse injury of the connective tissues located on the outer thigh and knee
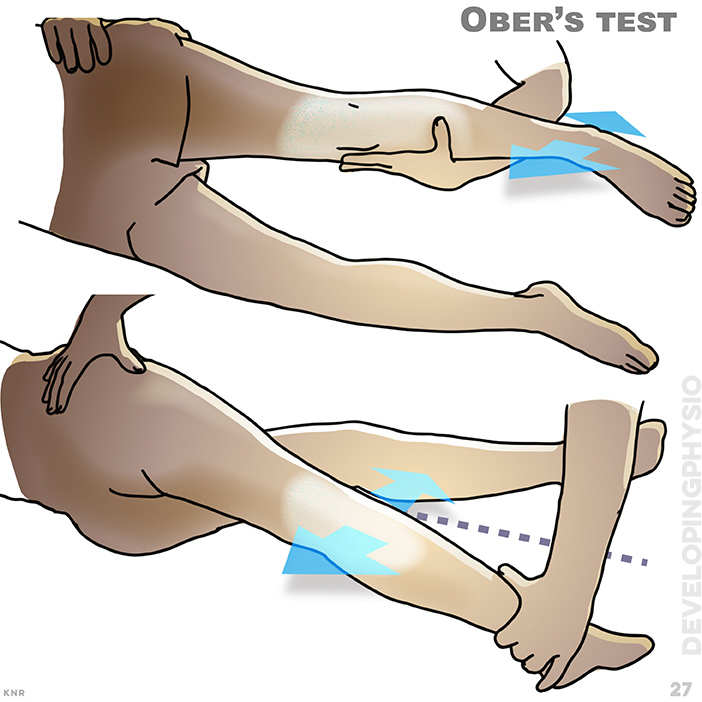
27. Ober’s test: Testing for ITB issues. A positive test is when the tested leg can’t pass below midline, with or without pain on the outside of the knee
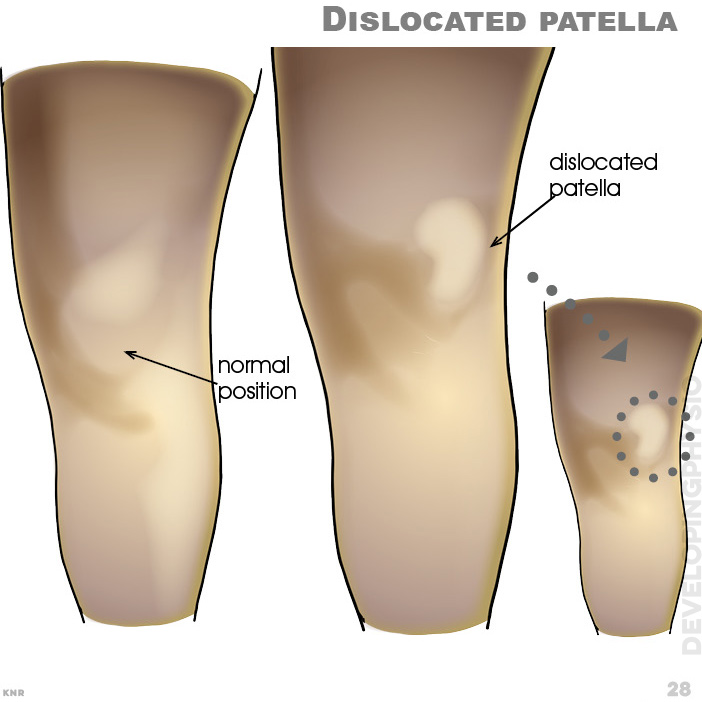
28. Dislocated patella, (normal position)
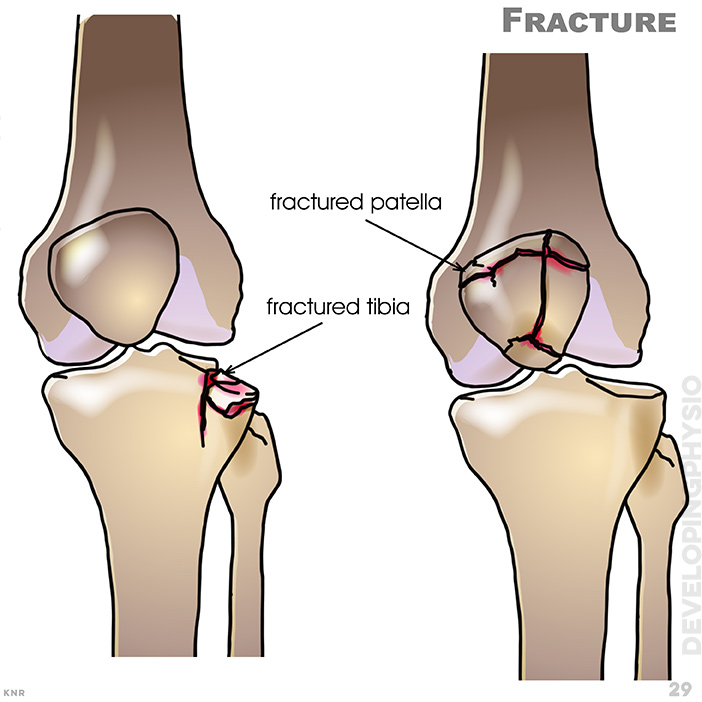
29. Fractured patella, fractured tibia
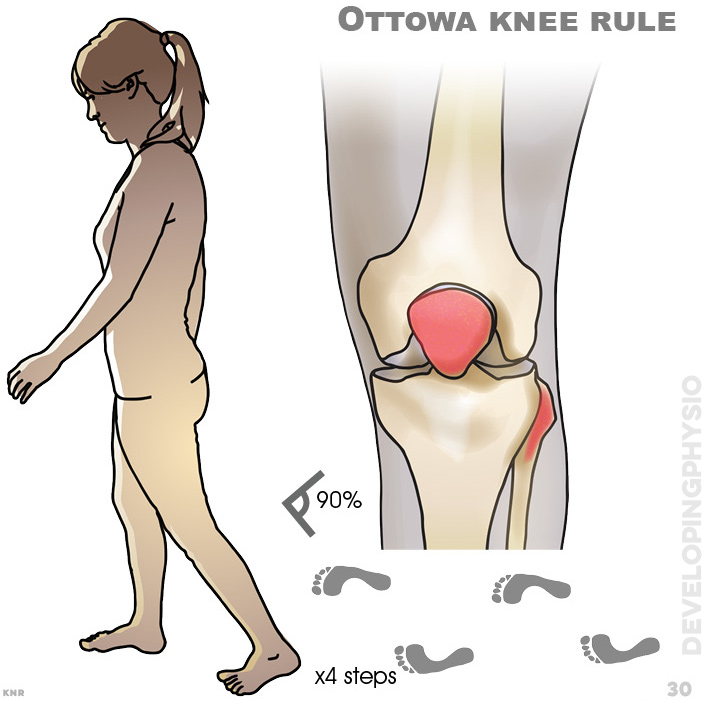
30. Ottawa knee rule to exclude fracture after high force trauma. If one of the following is present, an x-ray is recommended: Age over 55 yrs old . Pain on palpation patella . Pain on palpation head of fibula . Unable to flex knee more than 90 degrees. Unable to take 4 steps or unable to bear weight on legs